What is Screen Burn-In & Why Does it Happen?
Aug 5th 2022
Image burn-in affects all screen displays, including LCDs and OLEDs in mobile phones, monitors, wearable devices, televisions, and all electronic devices with a display screen. This article will cover everything you need to know about image burn-in and ways to mitigate it.
이 게시물에서 배울 내용은 다음과 같습니다:
What is Screen Burn-in?
Screen burn, also known as burn-in, occurs when a persistent image leaves a permanent ghost-like imprint on a display. While this issue is most commonly associated with OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays, LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays) can also experience a form of temporary image retention called image persistence. Understanding how different display technologies respond to prolonged static images is crucial for engineers designing applications in industrial, medical, and commercial environments.
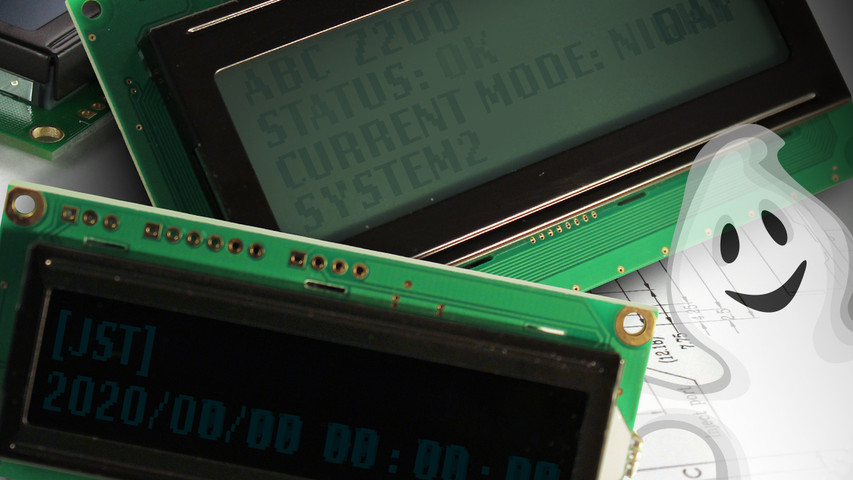
 LCD의 이미지 번인 예시.
LCD의 이미지 번인 예시.
번인 대 이미지 유지
Chances are you've encountered image burn-in and image retention before, but you didn't know which one you were seeing. They both have the same visual effects, so it's easy to mistake them for each other, but there's one key difference: image retention is temporary, and image burn-in is permanent.
We've seen many misleading articles, videos, and guides about "fixing" image burn-in or removing it from a display. Image burn-in is completely irreversible once it occurs on your display screen.
이 가이드에서는 대부분 이미지 보존의 작동 원리와 복구 프로세스의 속도를 높일 수 있는 방법을 설명합니다. LCD 및 OLED 디스플레이의 이미지 번인 및 이미지 보존에 대한 혼란을 해소하고자 합니다.
이미지 보존
고스팅 또는 이미지 지속성이라고도 하는 이미지 잔상은 일반적으로 몇 초의 짧은 시간 동안 LCD 또는 OLED에 이미지가 표시되는 일시적인 효과입니다.
How to tell the difference between image retention and screen burn-in?
이미지가 짧은 시간 후에 사라지는 경우 일시적인 이미지 보존 문제입니다. 이미지가 영구적으로 유지되면 이미지 번인이 발생한 것입니다.
Image retention doesn't require any intervention from the user to make it go away – it'll do that by itself. Retention will often occur before burn-in does on newer display technology like our TFTs and our new IPS displays.
Image retention will fade away, but there are some tips you can use to speed up the process. Simple actions like using a screen saver, cycling various graphics on the screen to exercise the pixels, and powering off the display whenever possible will help clear the image retention on your display.
이러한 방법은 이미지 번인을 '치료'한다고 광고하는 것과 동일한 방법이지만, 속지 마세요. 번인 현상에 대한 해결책은 없으며 번인 현상이 발생하지 않도록 연장하는 방법만 있습니다.
화면에 번인 손상이 있다고 생각하기 전에 다음 팁을 시도해보고 이미지 잔상인지 확인해 보세요. 이미지 잔상은 많은 화면에서 무해하고 흔하게 발생하는 현상입니다.
What Causes Screen Burn-in?
Screen burn-in is caused by screen pixels that stay activated in a static position for long periods of time. Think of a TV in a lobby or waiting area that's always playing the same news channel. The news channel footer and logo get burned into the screen permanently, even when you change the channel.
디스플레이 번인의 일반적인 원인으로는 정적 이미지, 메시지, 로고, 아이콘 등이 있습니다.
예를 들어 휴대폰에서 이미지 번인은 배터리, Wi-Fi 및 서비스 신호 아이콘이 영구적으로 고정된 위치로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다.
LCD 또는 OLED 픽셀이 정적인 위치에서 계속 활성화되어 있으면 결국 해당 위치에 "고정"됩니다. 이런 일이 발생하면 화면에 희미하고 고집스러운 이미지가 지속되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
LCD 및 OLED 디스플레이의 번인
번인의 결과는 모든 화면 유형에서 동일하게 보이지만 LCD와 OLED에서 발생하는 방식은 약간 다릅니다.
관련: OLED와 LCD의 차이점
LCD에서 번인이 발생하는 방식
정적 이미지를 장시간 표시하면 액정 디스플레이의 크리스탈이 움직이기 약해져 완전히 "켜짐" 위치에서 완전히 "꺼짐" 위치로 전환하기가 더 어려워집니다.
픽셀이 완전히 활성화 또는 비활성화되지 않으면 화면에서 선명하지 않은 흐릿한 이미지가 나타납니다. 이는 영숫자 문자가 업데이트되는 빈도가 낮은 문자 LCD를 사용하는 애플리케이션에서 흔히 발생합니다.
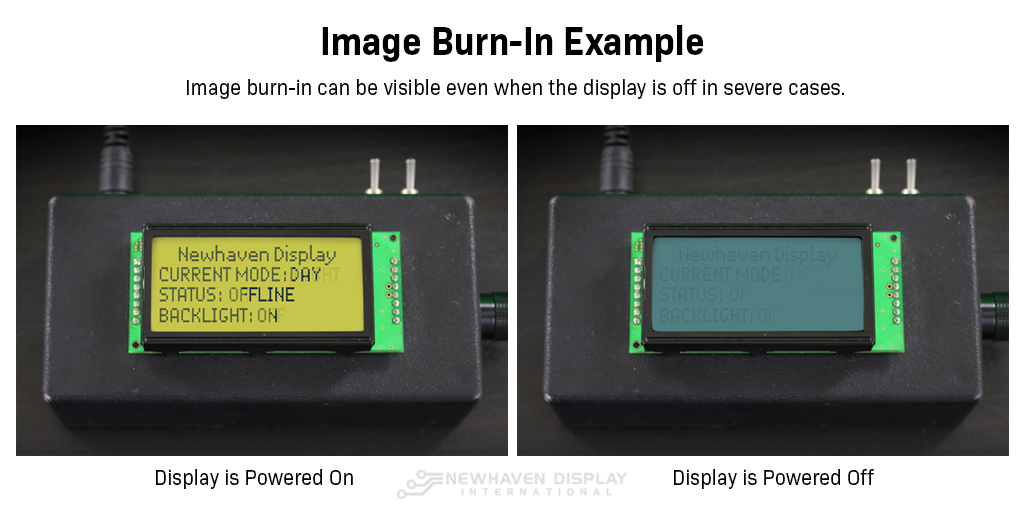
아래 예시에서는 디스플레이가 꺼진 후 LCD 화면에 남아있는 텍스트가 영구적으로 희미하게 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
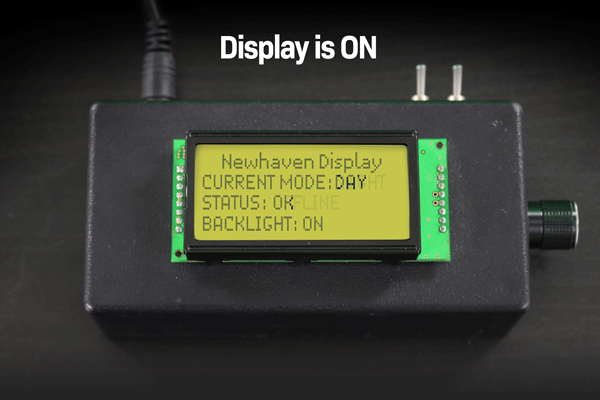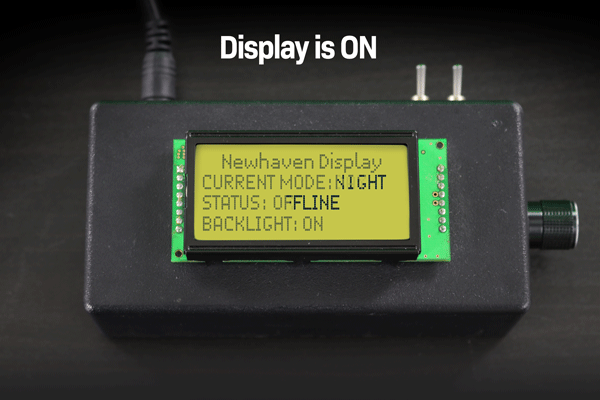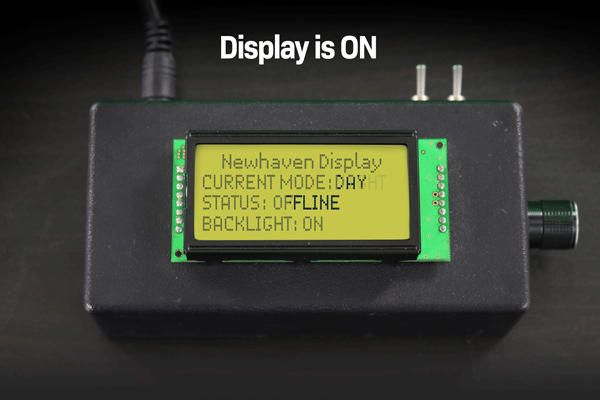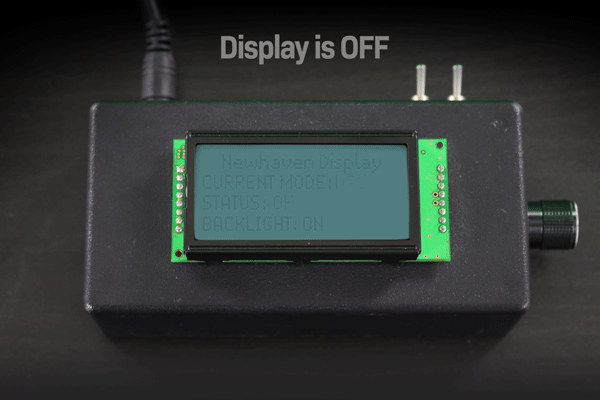 디스플레이를 켜고 끌 때 문자 LCD 이미지 번인의 예입니다.
디스플레이를 켜고 끌 때 문자 LCD 이미지 번인의 예입니다.
OLED에서 번인이 발생하는 방식
OLED는 백라이트가 필요 없다는 점에서 독특합니다. 디스플레이의 각 픽셀은 자체 발광 LED이므로 자체적으로 빛을 생성합니다. 그러나 픽셀은 시간이 지남에 따라 필연적으로 밝기가 떨어집니다. OLED 픽셀에 조명이 오래 비춰질수록 사용 빈도가 낮은 픽셀 옆의 픽셀은 더 어둡게 나타납니다.
정적 이미지가 OLED 디스플레이에 충분히 오래 머무르면 디스플레이에 완전히 다른 이미지가 표시되더라도 픽셀이 이전 이미지 뒤에 그림자를 남깁니다.
아래 예제에서 "Double Height" 텍스트가 OLED에 어떻게 레코딩되는지 확인하세요.
 OLED 이미지 번인 예시.
OLED 이미지 번인 예시.
기억하세요: 번인이 발생한 후에는 번인을 제거하거나 줄일 수 있는 방법이 없습니다. 장시간 또는 디스플레이를 재시작한 후에도 고집스러운 이미지가 지속된다면 이미지 번인 현상일 가능성이 높습니다.
Early Signs of LCD Screen Burn
LCDs don’t suffer from permanent burn-ins like OLEDs, but they can experience a temporary form known as image persistence. This occurs when a static image lingers faintly on the display even after the display content changes. Here are the early signs to watch for:
-
Ghosting or faint remnants of a previous image: If you can still see a shadow of a menu bar, logo, or other static content after switching screens, this is an indication of image retention.
-
Slow response time when transitioning images: If pixels take longer to refresh or adjust to new content, especially in high-contrast areas, your LCD may be experiencing early image persistence.
-
Color distortion in affected areas: Some parts of the display may appear slightly discolored or "washed out" after extended exposure to static content.
-
Variations across LCD types: IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels, commonly used for wide-viewing angles, are less prone to persistence than TN (Twisted Nematic) panels, which have faster response times but may exhibit minor retention effects.
If detected early, image persistence can be reversed by turning off the display or using a display refresh function. However, extended exposure to static content increases the risk of more stubborn retention.
LCD Applications Prone to Burn
While LCDs are less susceptible to permanent burn-in than OLEDs, certain industries rely on displays that frequently show static images, making them more prone to image persistence.
-
Medical Equipment Displays: Patient monitoring systems, diagnostic screens, and imaging devices often show static vital signs, graphs, or interface elements for extended periods, increasing the likelihood of image retention.
-
Industrial Control Panels: Factory automation screens, process control monitors, and instrumentation panels display static data, such as readouts and system statuses, for long durations.
-
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Retail checkout displays and kiosks frequently show the same user interface for hours, leading to uneven pixel wear.
-
Automotive and Marine Displays: Navigation systems, dashboard readouts, and infotainment screens may hold the same map or gauge interface for long periods, causing temporary retention.
-
Test and Measurement Devices: Oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and other laboratory instruments often feature fixed graphical elements, which can contribute to image persistence over time.
Newhaven Display’s TFT LCD modules are engineered with pixel-shifting technology, optimized brightness control, and advanced refresh techniques to minimize image retention. These design enhancements help extend the longevity and reliability of displays in mission-critical applications.
Early Signs of OLED Screen Burn
Unlike LCDs, OLED displays are more vulnerable to permanent burn-in due to their self-emissive pixels, which can degrade at different rates over time. Understanding the conditions that accelerate this process is essential for engineers designing long-lifespan products. Signs of OLED burn-in include:
-
Persistent ghost images: Static elements, such as logos or user interface (UI) components, remain visible even after switching displays, indicating pixel wear.
-
Uneven brightness levels: Frequently used areas may appear dimmer due to pixel aging, where some pixels degrade faster than others.
-
Color shifting or distortion: Affected regions may develop color imbalances, such as a reddish, yellowish, or bluish tint where burn-in has occurred.
-
Noticeable differences in high-contrast areas: Burn-in is most apparent where bright elements frequently overlay darker backgrounds, causing uneven luminance.
OLED Applications Prone to Burn
OLED displays offer vibrant colors and high contrast, making them ideal for many applications. However, certain use cases increase the likelihood of burn-in:
-
Medical and Diagnostic Displays: Patient monitoring systems and imaging equipment often maintain static readings and graphical elements.
-
Industrial and Automation Interfaces: Factory control displays frequently show persistent navigation menus and system statuses.
-
Handheld and Portable Devices: OLED-based test equipment, communication devices, and specialized tools often display static UI components.
-
Automotive and Aerospace Displays: Digital dashboards, heads-up displays (HUDs), and in-flight entertainment screens maintain fixed navigation elements and branding.
-
Retail and Commercial Signage: OLED advertising displays that feature static logos, pricing, or promotional graphics are at higher risk.
To mitigate OLED burn-in, Newhaven Display designs its OLED modules with pixel wear-leveling, automatic brightness adjustment, and built-in display refresh cycles. These features help extend the operational life of OLED displays used in high-contrast applications.
How to Test for Screen Burn
Detecting screen burn early can help prevent further pixel degradation. Here are a few methods to test for screen burn on LCD and OLED displays:
-
Full-Screen Color Tests: Displaying a solid color background (such as white, red, green, or blue) at full brightness can reveal ghost images or uneven pixel wear.
-
Gradient and Gray Screen Tests: Viewing a gradient pattern or a uniform gray background can help detect subtle color shifts, which may indicate early signs of burn-in.
-
Switching Between High-Contrast Images: Quickly alternating between bright and dark images can make burn-in effects more noticeable, especially in frequently used areas of the display.
-
Using Specialized Burn-in Test Tools: Some diagnostic applications generate test patterns designed to highlight persistent image retention or OLED burn-in.
If mild image retention is detected, running a pixel refresh cycle, adjusting brightness levels, or using a screen saver can help reduce visibility. However, permanent burn-in on OLED displays cannot be reversed, making proactive prevention the best approach.
Ways to Mitigate/Avoid Screen Burn-in
아무리 최신 디스플레이라도 언젠가는 번인이 발생하지만 번인이 발생하기 전에 화면의 수명을 연장할 수 있는 몇 가지 간단한 조치가 있습니다. 적절한 방법을 사용하면 번인 현상 없이 디스플레이에서 수년간 뛰어난 성능을 얻을 수 있습니다.
How to avoid screen burn-in
- 사용하지 않을 때는 디스플레이 전원 끄기
- 화면 보호기 사용
- 픽셀 운동(회전 또는 스크롤 효과)
- 화면 밝기 또는 대비 낮추기
관련: 전자 디스플레이 청소 방법
알고 계셨나요? 화면 보호기는 화면 번인을 완화하기 위한 적극적인 방법이었던 원래의 목적에서 그 이름이 유래되었습니다.
사용하지 않을 때는 디스플레이 전원 끄기
경우에 따라 "항상 켜져 있는" 디스플레이가 필요하거나 디스플레이를 장시간 켜져 있어야 하는 경우가 있다는 것을 알고 있습니다.
기회가 된다면 디스플레이의 전원을 완전히 껐다 켜세요. 이렇게 하면 픽셀이 재설정되고 번인을 방지하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
전원 사이클을 사용할 수 없는 경우 디스플레이 켜기/끄기 명령을 사용하여 디스플레이를 끌 수 있습니다. 또는 디스플레이 데이터를 RAM에 유지하면서 디스플레이를 절전 모드로 전환할 수 있습니다.
화면 보호기 사용
화면 보호기는 디스플레이를 끌 수 없는 경우 좋은 대안이 될 수 있습니다. 항상 켜져 있을 필요가 없는 디스플레이의 경우 사용하지 않을 때는 화면을 쉬게 두는 것이 좋습니다.
화면 보호기 또는 절전 모드를 사용하면 장치의 전원을 완전히 껐다가 다시 켜는 것보다 빠르게 시작할 수 있습니다.
픽셀 연습하기
픽셀을 움직이게 하세요! 픽셀이 정적인 위치에서 활성화된 상태로 오래 있을수록 픽셀이 번인에 가까워집니다. 텍스트 스크롤, 이미지 이동 또는 색상 변경을 통해 화면의 픽셀을 움직일 수 있습니다.
이 기술은 자동차의 타이어를 회전시키는 것과 매우 유사합니다. 목표는 디스플레이 전체에 마모를 고르게 분산시키는 것입니다.
화면 밝기 또는 대비 낮추기
가능하면 화면 밝기를 낮추세요. 조명(밝기)이 높을수록 더 많은 전류가 필요하므로 LED 수명이 단축됩니다.
OLED 디스플레이의 경우 명암비를 낮추면 밝기가 낮아지고 이미지가 번지는 속도가 감소합니다. 조도(밝기)를 높이려면 더 많은 전류가 필요하므로 OLED 픽셀 수명이 단축됩니다.
LCD 디스플레이의 경우 명암비를 낮추면 액정에 가해지는 스트레스가 줄어들고 픽셀이 약해지거나 달라붙는 비율을 줄이는 데 도움이 됩니다.
LCD 및 OLED 번인에 관한 모든 것 - [동영상]
Find more helpful videos like this on our YouTube channel.
결론
이미지 번인은 되돌릴 수 없으며 한 번 발생하면 수정할 수 없다는 점을 기억하세요. 스크롤 효과, 픽셀 회전, 화면 보호기 사용, 사용하지 않을 때 화면 끄기 등 디스플레이의 수명을 연장하는 데 도움이 되는 이미지 번인 방지 대책을 수립하는 것이 필수적입니다.