Tocco capacitivo e tocco resistivo
Touchscreen displays have become a standard piece of technology in our daily lives. Many LCD and OLED applications now include touchscreen technology to improve functionality or enhance user experience.
Tuttavia, non esiste un touchscreen universale per ogni applicazione. Dovrete decidere quale touchscreen è adatto al vostro progetto. Come decidere tra OLED e LCD, la scelta del touch screen giusto dipenderà dai requisiti della vostra applicazione.
Correlato: Dettagli e guida all'integrazione del touch panel
In questo articolo:
Display touchscreen capacitivi
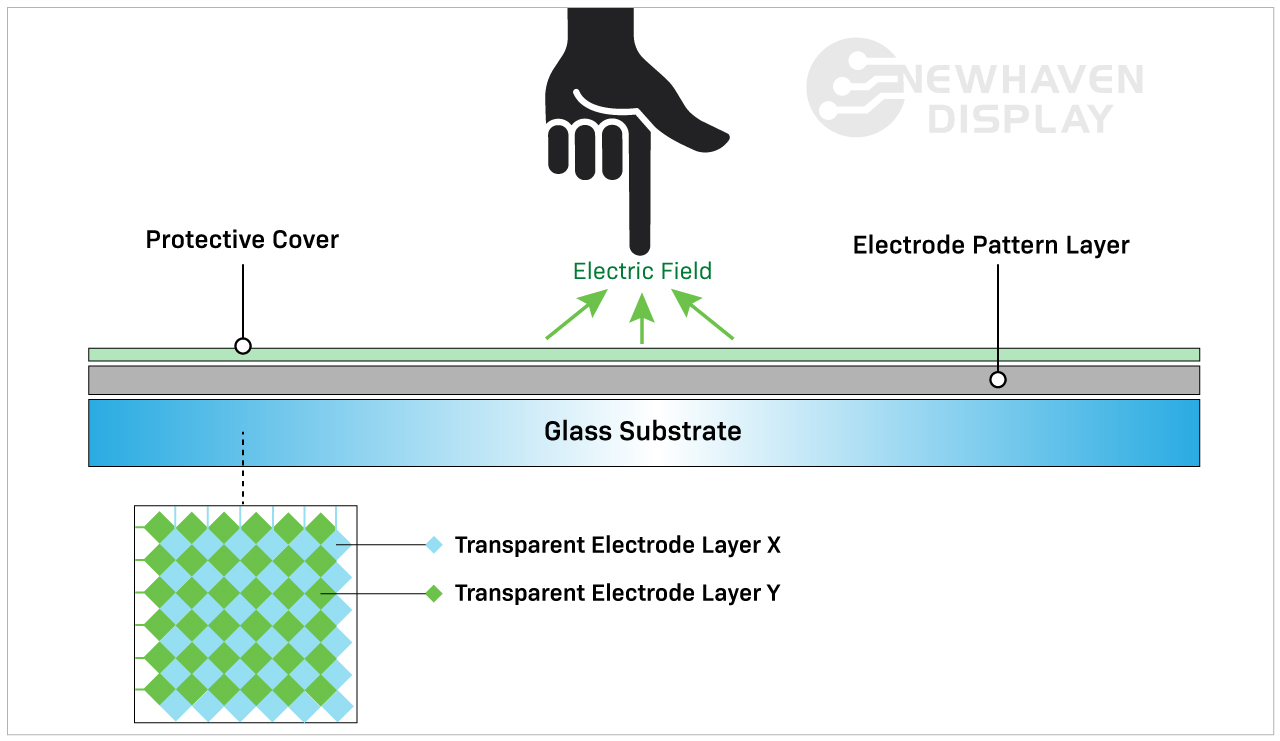
Un pannello touchscreen capacitivo è costituito da un isolante, solitamente vetro, rivestito da un conduttore trasparente. Idisplay touchscreen capacitivi rispondono a input conduttivi come un polpastrello e non richiedono una pressione per attivare un "evento tattile".
I touch panel capacitivi sono l'opzione touchscreen più moderna e avanzata grazie alle loro capacità avanzate. Si trovano comunemente in prodotti di consumo come smartphone, tablet, elettrodomestici e monitor.
Correlato: Cos'è un display IPS
Come funzionano i touchscreen capacitivi?
Un touchscreen capacitivo rileva e risponde alle variazioni di capacità causate dal campo elettrostatico dello schermo quando la superficie dello stesso viene toccata.
Vantaggi del touchscreen capacitivo
I display touchscreen capacitivi consentono di eseguire gesti tattili e di rispondere agli input multi-touch. In genere è possibile immettere da uno a cinque input tattili contemporaneamente, ma alcuni touchscreen capacitivi sono in grado di elaborarne un numero ancora maggiore.
Gli schermi tattili capacitivi offrono immagini più luminose e con un contrasto più elevato grazie alla composizione dei loro pannelli. I display con touch screen capacitivi sono più resistenti di quelli resistivi perché sono progettati con un vetro di copertura sullo strato superiore. Infatti, tutti i nostri display TFT capacitivi hanno un vetro di copertura incorporato di 0,7 mm di spessore e possono essere ulteriormente personalizzati per una maggiore durata. personalizzati per una maggiore durata.
Correlato: Prova d'urto del vetro del coperchio LCD
Svantaggi del touchscreen capacitivo
Il costo di un touchscreen capacitivo è leggermente superiore a quello di un pannello touchscreen resistivo a causa dei processi di produzione più complicati.
Sebbene il costo sia attualmente superiore a quello dei touchscreen resistivi, i touchscreen capacitivi stanno rapidamente diventando lo standard industriale della tecnologia touchscreen.
La maggiore reattività può essere uno svantaggio a seconda di come e dove viene utilizzato il display. Ad esempio, un touchscreen capacitivo non risponderebbe facilmente all'utente quando indossa alcuni tipi di guanti. Sebbene i touchscreen capacitivi non rispondano a input inorganici, possono comunque essere attivati accidentalmente da altri elementi conduttivi. Uno degli elementi più comuni che causano interruzioni è l'acqua.
La pioggia, l'umidità e la condensa sulla superficie degli schermi tattili capacitivi causano spesso immissioni accidentali e una minore precisione finché l'acqua non viene rimossa. Questo è uno dei motivi principali per cui in certe situazioni si preferisce un touchscreen resistivo a uno capacitivo.
Correlato: Tipi di schermo LCD
Quando scegliere un touchscreen capacitivo
Qualsiasi dispositivo che utilizzi gesti tattili come lo scorrimento, il pizzicamento o il multi-touch richiede un touchscreen capacitivo. Queste caratteristiche spesso rendono i display touchscreen capacitivi più intuitivi e facili da usare rispetto ai touchscreen resistivi. I touchscreen capacitivi sono i più adatti per le applicazioni che richiedono una maggiore reattività al tocco e una migliore luminosità e contrasto dell'immagine.
Display touchscreen resistivi
I pannelli touchscreen resistivi rilevano la pressione sullo strato superiore del display e inviano un segnale al circuito per attivare la funzionalità del touchscreen. Poiché utilizzano la pressione per attivare gli input tattili, i display touchscreen resistivi possono essere utilizzati con stilo, guanti e altri oggetti. Gli schermi tattili resistivi sono costruiti senza vetro di copertura e in plastica, il che li rende più suscettibili ad ammaccature e graffi.
I pannelli tattili resistivi sono stati i primi touchscreen a entrare nel mercato e sono ancora ampiamente utilizzati.
Come funzionano i touchscreen resistivi?
Gli schermi tattili resistivi sono costituiti da due strati di rivestimento resistivo con uno strato di spazio tra di essi. A "evento tattile" si verifica quando questi due strati entrano in contatto tra loro (chiudendo il circuito) grazie all'azione dell'utente che preme sullo strato superiore morbido e semi-flessibile. Ogni strato è costituito da linee orizzontali e verticali (matrice x,y) che rilevano la posizione esatta del tocco.
L'intercapedine o strato spaziale è tipicamente costituito da aria o gas inerte e da alcuni distanziatori il cui unico scopo è quello di separare lo strato superiore morbido dallo strato inferiore.

Vantaggi del touchscreen resistivo
I touchscreen resistivi sono spesso considerati la varietà meno avanzata di touch panel rispetto ai touch panel capacitivi. Tuttavia, la possibilità di interagire con input non organici rende questi touchscreen rilevanti in settori specifici.
I display touchscreen resistivi sono meno sensibili di quelli capacitivi. In alcuni casi questo è considerato un vantaggio ed è il motivo per cui vengono scelti per applicazioni specifiche. Gli schermi touchscreen resistivi non rispondono a input accidentali provenienti dall'ambiente circostante, quindi non vengono interrotti da fenomeni quali versamenti d'acqua o detriti leggeri che finiscono sullo schermo.
Questo tipo di touchscreen richiede un maggior numero di input intenzionali da parte dell'utente, rendendoli più affidabili in ambienti difficili e instabili. Ad esempio, un touchscreen resistivo è la soluzione perfetta in un cantiere dove acqua o detriti potrebbero finire sullo schermo. Sono anche la migliore opzione di display touchscreen per le situazioni in cui l'utente indossa i guanti.
Svantaggi del touchscreen resistivo
I pannelli touchscreen resistivi sono purtroppo più soggetti ad ammaccature e graffi. La scarsa visibilità alla luce diretta del sole non li rende ideali per le applicazioni all'aperto. La loro incapacità di rispondere agli input multi-touch può essere uno svantaggio nelle applicazioni veloci che lo richiedono. Poiché gli schermi tattili resistivi si basano sulla pressione applicata allo strato superiore, tendono a essere abusati e maneggiati male, il che li rende meno durevoli nel tempo rispetto agli schermi tattili capacitivi.
Correlato: Come pulire un display elettronico
Quando scegliere un touchscreen resistivo
La tecnologia touchscreen resistiva è ideale per le applicazioni a basso costo che prevedono ambienti difficili, luce solare indiretta e funzioni touch semplici. Il minor numero di tocchi accidentali, la migliore resistenza al calore e all'umidità e la possibilità di utilizzare praticamente tutto (stilo, penna, guanti, dita, ecc.) rendono questa tecnologia touchscreen una soluzione più affidabile quando l'input dell'utente è fondamentale.
Tabella di confronto tra capacitivo e resistivo
| Capacitivo | Resistivo | |
| Tipo di attivazione | Tatto leggero (conduttivo) | Tocco di pressione |
| Costo | Costi di produzione più elevati | Costi di produzione inferiori |
| Sensibilità al tocco | Più sensibile | Meno sensibile |
| Luminosità e contrasto | Il meglio | Buono |
| Durata | Il meglio | Buono |
| Capace di multi-touch | Sì | No |
| Si possono usare guanti, penna o stilo? | Sì (ma in misura limitata) | Sì |
| Utilizzi | Applicazioni multi-touch e precise. | Ambienti robusti con funzioni touch semplici. |
Conclusione
Sebbene sia chiaro che i touchscreen capacitivi stanno dominando il mercato dell'elettronica di consumo, i touchscreen resistivi hanno ancora un vantaggio per certi versi.
Se siete alla ricerca di un touchscreen economico che possa funzionare con semplici input a sfioramento in ambienti difficili, il resistivo è la scelta giusta. Per una tecnologia touchscreen più avanzata e intuitiva con applicazioni di qualità superiore, scegliete i touchscreen capacitivi.
Per saperne di più sui display touchscreen o su tutto ciò che riguarda la tecnologia dei display, siamo sempre a disposizione! Contattate inostri tecnici oggi stesso.
Ultimi post del blog
-
How to Display Images on a TFT LCD
TFT LCDs, or thin-film transistor liquid-crystal displays, are a type of LCD commonly used in var …Apr 2nd 2024 -
Brightness Enhancement Film (BEF)
Over the years, display manufacturers have been developing new technologies to improve image qual …Mar 6th 2024 -
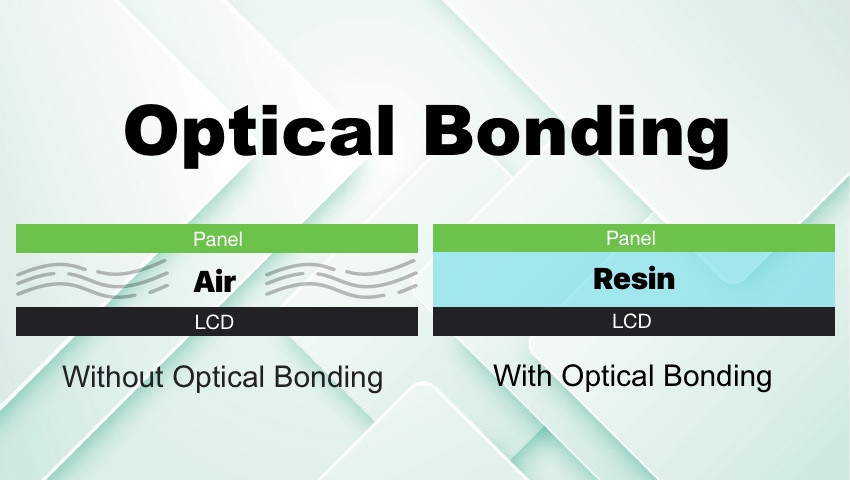
Incollaggio ottico
Many applications, particularly in harsh environments, require specific modifications to their el …Feb 7th 2024