TN vs IPS - What's The Difference?
In display technologies, TN (Twisted Nematic) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) are two terms that often arise. Both are types of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technologies, but they differ in construction, performance, and suitable applications.
Understanding the differences between TN and IPS in LCDs is essential for consumers and professionals when selecting a display that meets their specific requirements.
In this Article:
How LCDs Work
Unlike OLED screens, whose pixels emit their own light, LCD screens need a light source because their pixels can't emit light. This light source is called a backlight. This backlight must be controlled to turn individual pixels on/off via liquid crystals.
Related: What is the difference between OLEDs and LCDs
What are liquid crystals?: Liquid crystals are substances that flow like a liquid but have molecules that can be oriented in a particular direction, like a crystal.
The main job of the liquid crystals in an LCD screen is to control how this light travels through the screen to show the image you see. Imagine the liquid crystals as tiny shutters that can open and close. When they receive electric signals, they move and change how they let light pass through them. This is like adjusting blinds in a window to control how much sunlight comes in.
Learn more: Types of LCDs
The way these liquid crystals move and align themselves can be different in various types of screens. This is where TN and IPS LCDs come in.
TN (Twisted Nematic) Displays
TN displays are a type of LCD technology characterized by offering low power consumption, high response, and refresh rates compared to IPS displays. In TN displays, the liquid crystals are aligned perpendicularly to the panel plane and twist when a voltage is applied, altering the light's polarization and the visibility of the pixel. This structure allows TN panels to change states quickly, making them ideal for applications requiring fast motion, such as competitive gaming monitors.
However, this design typically offers narrower viewing angles and less accurate color reproduction than IPS displays. TN technology is widely adopted in budget-friendly monitors and screens where high refresh rates are more critical than color accuracy.
Who invented TN LCD technology?
In 1970, physicists Martin Schadt and Wolfgang Helfrich at Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd in Basel, Switzerland, created the twisted nematic field effect, revolutionizing the development of LCDs still used today.
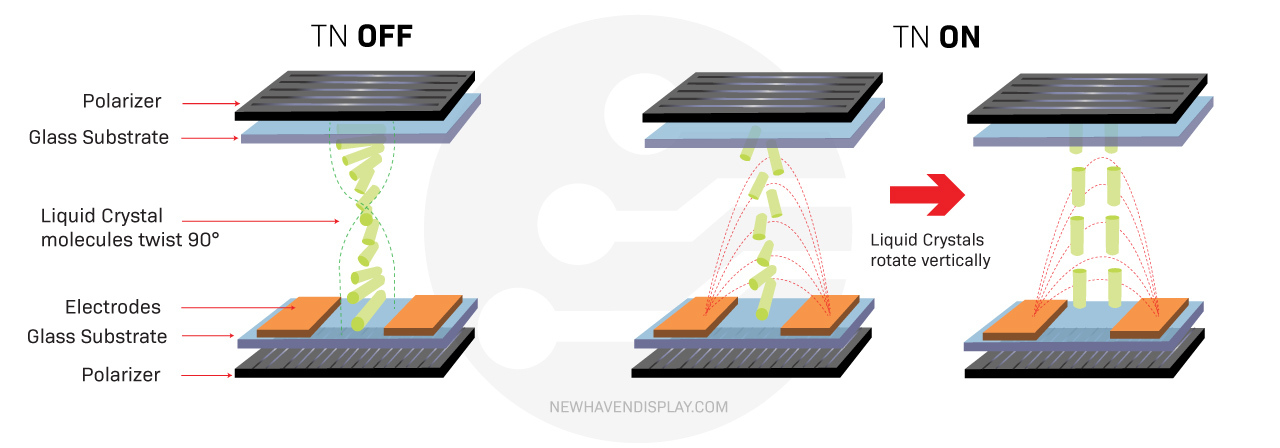
How Liquid Crystals Work in TN LCDs:
In TN panels, the liquid crystals are aligned in a helix (spiral) structure. When no voltage is applied, this twist lets light pass through the display layers. Applying voltage makes the crystals partially untwist, changing their angle and obstructing the light to varying degrees. This controlled light modulation interacts with the final polarizing filter, determining how much light reaches your eyes and creating different levels of brightness and color for each pixel.
Advantages of TN LCDs:
- High refresh rates: TN panels offer very high refresh rates, making them a preferred choice for competitive gaming where fast refresh rates are crucial for a smooth gaming experience.
- Fast response times: TN displays offer the fastest response times among LCD panel types. This minimizes motion blur and ghosting in fast-paced visual content, ideal for gaming and dynamic video playback.
- Lower cost: Compared to IPS and VA panels, TN displays are more affordable, offering a cost-effective solution for budget-conscious consumers and in situations where color accuracy is not a primary concern.
- Energy efficiency: TN panels generally consume less power than their IPS counterparts, making them more energy-efficient and suitable for devices where power consumption is important.
Disadvantages of TN LCDs:
- Color accuracy and consistency: TN panels have lower color accuracy and inferior color reproduction compared to IPS displays, making them less ideal for precise color management, such as photo editing or graphic design.
- Narrow viewing angles: One of the most significant drawbacks of TN panels is their limited viewing angles, especially vertically. Colors and contrast can shift significantly when viewed from off-angles.
- Inferior black levels and contrast: Compared to IPS and VA panels, TN displays often struggle to reproduce deep blacks, resulting in lower overall contrast ratios.
- Less effective in direct sunlight: TN panels usually don't perform as well as IPS displays in direct sunlight. The limited viewing angles and contrast can reduce visibility in bright conditions.
Learn more: Transmissive vs Reflective vs Transflective LCD Modes
TN LCDs Applications
TN (Twisted Nematic) displays are particularly suited for specific applications due to their unique characteristics, such as high refresh rates, fast response times, and low power consumption.
Everyday Applications Powered by TN Displays
- Gaming devices: Their high refresh rates and the lowest response times reduce motion blur and ghosting, providing a competitive edge in fast-paced games even if it comes at the cost of viewing angles and color accuracy. TN displays are commonly found in arcade games, portable gaming consoles, and e-tournament screens.
- Consumer devices: TN displays are a popular choice for budget-friendly consumer devices such as computers, mobile phones, e-readers, calculators, multimeters, printers, refrigerators, washers, and microwaves due to their lower cost than IPS and VA panels.
- Low-power applications: TN displays' low power consumption can be beneficial for extended battery life in IoT (Internet-of-Things) devices, wearable devices, and portable medical devices such as blood pressure monitors and glucometers.
- Commercial/industrial equipment: TN screens are widely used in industrial control panels, CNC machines, robots, air quality sensors, building automation systems, oscilloscopes, aircraft panels, temperature gauges, and various commercial and industrial equipment and devices.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) Displays
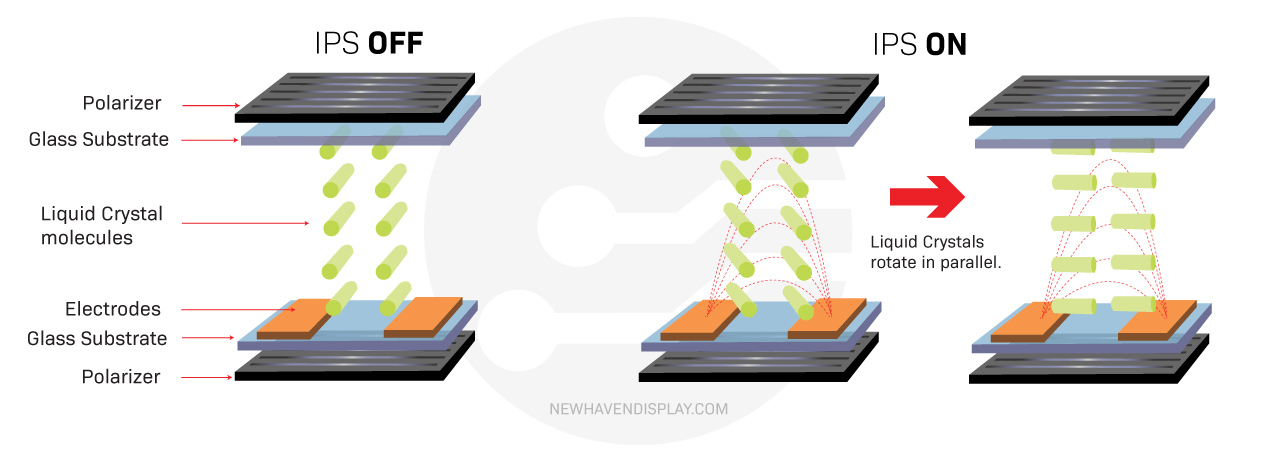
IPS displays are a type of LCD technology characterized by their ability to offer better color reproduction and wider viewing angles compared to TN LCD panels. In IPS displays, the liquid crystals are aligned in parallel to the panel plane, which allows for more consistent and accurate color representation from different viewing angles. This technology is commonly used in high-end monitors, televisions, and mobile devices for its superior image quality and color accuracy.
How Liquid Crystals Work in IPS LCDs:
In IPS panels, the liquid crystals are aligned horizontally, unlike the twisted structure of TN panels. When no voltage is applied, the crystals let light pass through. Applying voltage makes the crystals tilt slightly within the plane, altering the light's polarization. This controlled polarization change interacts with the final filter, dictating how much light reaches the viewer and thereby affecting the brightness and color of each pixel.
Advantages of IPS LCDs:
- Color accuracy and consistency: IPS displays deliver the most accurate and consistent color reproduction among LCD panel types, such as TN and VA displays. This makes them ideal for photography, graphic design, and other color-critical work.
- Wide viewing angles: IPS displays show very little shift in color and contrast, even when viewed from different viewing angles.
- Fast Response Times: While not as fast as TN panels, IPS displays offer response times sufficient for most users. This ensures smooth visuals during motion or fast-paced content.
- Good Sunlight Visibility: Compared to TN panels, IPS displays typically offer better readability in direct sunlight due to their wider viewing angles and reduced reflection.
Disadvantages of IPS LCDs:
- Higher Cost: IPS panels are generally more expensive than TN and VA panels, especially in larger sizes.
- Backlight Bleeding: Some IPS panels may exhibit backlight bleeding, where light seeps from the edges of the display, especially in dark scenes.
- Slower Response Times than TN Panels: For gamers or users requiring the fastest response times for competitive esports or high-refresh-rate displays, TN panels might be a better choice.
IPS LCDs Applications
IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays are especially well-suited for a range of applications, thanks to their distinctive features like superior color accuracy, wide viewing angles, and consistent color performance.
Everyday Applications Powered by IPS Displays
- High-end electronics: IPS displays are frequently used in mid-range to high-end electronic devices such as smartphones, dashcams, portable cameras, laptops, TVs, and computer monitors,
- Professional display monitors: Consistent color performance across different viewing angles makes IPS panels suitable for ATMs, photography studios, advertising screens, ultrasound, and MRI machines.
- Graphic design and media: IPS screens are widely used in web and graphic design, movie studios, and virtual/augmented reality devices due to their high picture quality.
- Industrial equipment: IPS displays are commonly used in PLCs, robotics, testing equipment, and automation systems to show operational data, alarms, and process diagrams that require excellent visibility from different viewing angles.
Learn more: Capacitive vs Resistive Touchscreens
TN vs IPS
TN panels are known for their speed, but have narrower viewing angles and less accurate color reproduction compared to IPS displays. IPS displays offer precise color accuracy and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for professional design and photography.

TN vs IPS Comparison Table
| TN Displays | IPS Displays | |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Generally less expensive | Typically more expensive |
| Viewing Angles | Narrower | Wide |
| Color Accuracy | Less accurate | Superior |
| Black Levels | Lower | Good |
| Contrast Ratio | Lower | Higher |
| Response Time | Faster | Slower |
| Refresh Rate | Higher | Generally lower than TN, but improving |
| Power Consumption | Typically lower | Slightly higher |
| Uses |
|
|
Explore Our Display Solutions: from industry-standard TN LCDs to cutting-edge IPS panels, we have the perfect display for your specific needs. Need a custom LCD or OLED? We specialize in crafting custom display solutions engineered to bring your specific vision to life.
Conclusion
When deciding between TN or IPS displays, it is important to consider your priorities since both options offer great features. If you prioritize affordability and performance in fast-paced games, a TN panel might be the best choice for you. However, if you value color accuracy, wide viewing angles, and a more immersive experience for creative work or media consumption, then an IPS panel is a better option.
Latest Blog Posts
-
US2066 Tutorial: Character Slim OLED with Arduino
If you are interested in getting started with character OLED displays using the US2066 controller …Jul 18th 2024 -
Passive Matrix vs Active Matrix - A Beginner's Guide
Have you ever wondered how display screens are able to produce sharp images and vibrant colors? T …May 30th 2024 -
How to Display Images on a TFT LCD
TFT LCDs, or thin-film transistor liquid-crystal displays, are a type of LCD commonly used in var …Apr 2nd 2024