Rodzaje LCD
Sep 15th 2022
Ekrany ciekłokrystaliczne (LCD) są podstawą rynku wyświetlaczy cyfrowych i są używane w aplikacjach wyświetlających w każdej branży. Ponieważ każda aplikacja wyświetlacza przedstawia unikalny zestaw wymagań, wybór specjalistycznych ekranów LCD wzrósł, aby sprostać tym wymaganiom.
Ekrany LCD można pogrupować na trzy kategorie: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching) oraz VA (Vertical Alignment). Każdy z tych typów ekranów ma swoje unikalne cechy, z których prawie wszystkie mają związek z tym, jak obrazy pojawiają się na różnych typach ekranów.
W tym artykule:
- TN (Twisted Nematic)
- VA (Vertical Alignment)
- IPS (In-Plane Switching)
- Tabela porównawcza TN vs VA vs IPS
- Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
- Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
- Things to Consider
- Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
- Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
- Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
- Wniosek
Powiązane: OLED vs LCD
It's worth noting that although these screen types belong to the LCD screen type, they use thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology which is a variant of the standard LCD screen type.
Główne cechy różniące typy ekranów LCD to jasność, kąty widzenia, kolor i kontrast.
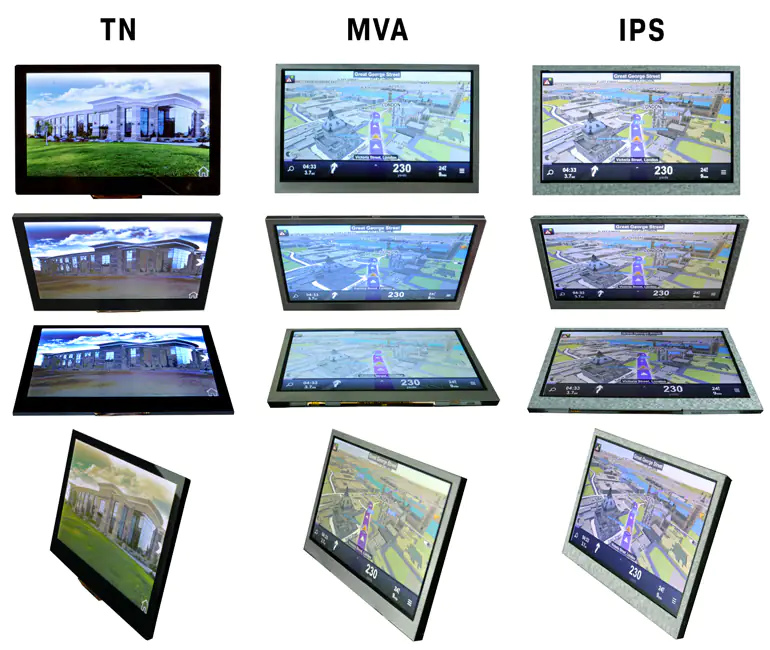
TN (Twisted Nematic)
Technologia ta składa się z nematycznych ciekłych kryształów umieszczonych pomiędzy dwoma płytami szkła. Gdy do elektrod zostanie przyłożone zasilanie, ciekłe kryształy obracają się o 90°. Wyświetlacze LCD typu TN (Twisted Nematic) są najczęściej spotykanym typem ekranów LCD. Oferują one obrazy w pełnym kolorze i umiarkowane kąty widzenia.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one, TN LCDs have faster response times and refresh rates than other TFT LCDs.
Wyświetlacze TN TFT są bardzo popularne wśród społeczności graczy, gdzie dokładność i szybkość reakcji może stanowić różnicę między wygraną a przegraną.
Częstotliwość odświeżania i czas reakcji odnoszą się do czasu potrzebnego pikselom do aktywacji i dezaktywacji w odpowiedzi na dane wprowadzone przez użytkownika; jest to kluczowe dla szybko poruszających się obrazów lub grafik, które muszą być aktualizowane tak szybko, jak to możliwe, z niezwykłą precyzją.
Wyświetlacze TN pozostają popularne dzięki niezawodnej wydajności i korzystnej cenie.
TN LCD Charakterystyki

-
Ekonomiczny
Skręcone ekrany nematyczne były tradycyjnie najbardziej opłacalną opcją LCD.
-
Najwyższa częstotliwość odświeżania
Ekrany LCD TN mają najwyższą częstotliwość odświeżania i czas reakcji.
-
Ograniczone kąty widzenia
Ekrany TN LCD mają średnie kąty widzenia 45-65 stopni.
-
Ograniczona jasność
Ekrany LCD TN nie są wystarczająco jasne do oglądania na zewnątrz lub w bezpośrednim świetle słonecznym.
VA (Vertical Alignment)
VA, znane również jako Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment (MVA) dislays oferują cechy spotykane zarówno w ekranach TN, jak i IPS. Piksele w wyświetlaczach VA ustawiają się pionowo do szklanego podłoża po przyłożeniu napięcia, umożliwiając przejście światła.
Wyświetlacze z ekranami VA zapewniają szerokie kąty widzenia, wysoki kontrast i dobre odwzorowanie kolorów. Zachowują wysoką szybkość reakcji podobną do ekranów TN TFT, ale mogą nie osiągać takich samych poziomów jasności czytelnej w świetle słonecznym jak porównywalne ekrany TN lub IPS LCD. Wyświetlacze VA są generalnie najlepsze do zastosowań, które muszą być oglądane pod wieloma kątami, takich jak cyfrowe oznakowanie w środowisku komercyjnym.
VA LCD Charakterystyka
-
Szeroki kąt widzenia
Ekrany VA oferują szersze kąty widzenia niż LCD TN.
-
Kolory i kontrast
Ekrany LCD VA mają poprawione kolory i kontrast w porównaniu do TN TFT.
-
Podświetlenie Jasność
Ekrany LCD VA mają tendencję do oferowania niższej jasności niż równoważny model TFT w technologii TN.
-
Pobór mocy
Wyświetlacze LCD odczytywane w świetle słonecznym mogą zużywać więcej energii niż standardowe ekrany LCD.
IPS (In-Plane Switching)
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
Powiązane: Co to jest wyświetlacz IPS?
IPS przewyższa wyświetlacze TN w każdej ważniejszej kategorii.
IPS is superior in contrast, brightness, viewing angles, and color representation compared to TN screens. Images on screen retain their quality without becoming washed out or distorted, no matter what angle they’re viewed from. Because of this, viewers have the flexibility to view content on the screen from almost anywhere rather than having to look at the display from a front-center position.
IPS pozwala uzyskać kolorowe, dokładne i ostre obrazy oglądane pod niemal każdym kątem.
Wyświetlacze IPS oferują nieco niższą częstotliwość odświeżania niż wyświetlacze TN. Pamiętaj, że czas przejścia pikseli z nieaktywnego do aktywnego jest mierzony w milisekundach. Dla większości użytkowników różnica w częstotliwości odświeżania będzie więc niezauważalna.
Charakterystyka IPS LCD
-
Cena pkt.
Wyświetlacze IPS są obecnie bardziej opłacalne, porównywalne z wyświetlaczami TN LCD.
-
Średnia częstotliwość odświeżania
Ekrany IPS mają wolniejsze częstotliwości odświeżania i czasy reakcji niż ekrany LCD TN.
-
Najszersze kąty widzenia
Ekrany IPS LCD mają najszersze kąty widzenia spośród wszystkich ekranów TFT LCD.
-
Best Colors
Ekrany IPS LCD wytwarzają najdokładniejsze, żywe kolory spośród wszystkich ekranów TFT LCD.
-
Najwyższa jasność
Ekrany LCD IPS mają podświetlenia o wysokiej jasności, dzięki czemu można je odczytać w świetle słonecznym.
Tabela porównawcza TN vs VA vs IPS
| TN | VA | IPS | |
| Jasność | Lepiej | Dobra | Najlepsza |
| Wydajność | Najszybciej | Szybko | Szybko |
| Kąt widzenia | Dobra | Lepiej | Najlepsza |
| Kolor | Dobra | Lepiej | Najlepsza |
| Kontrast | Dobra | Najlepsza | Lepiej |
| Poziomy czerni | Dobra | Najlepsza | Lepiej |
| Jakość obrazu | Dobra | Lepiej | Najlepsza |
| Wykorzystuje | Gaming ze względu na wydajność | Ogólne zastosowanie ze względu na cenę i jakość | Profesjonalne, gdzie wymagana jest jakość |
Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
Standard LCDs are ideal for straightforward applications where simplicity, longevity, and low power consumption are key. TFT LCDs deliver enhanced visuals and interactivity, making them better suited for versatility or graphic-rich interfaces. Choosing between them depends on your project’s design priorities, environment, and user needs.
Monochrome
Monochrome LCDs use one color for display content, typically black or blue on a light background. They are optimized for basic communication needs, offering strong visibility, extended product life, and efficient power use. These displays are a reliable fit for designs where function matters more than form.
Multi-Color
Multi-color LCDs display content in two or more predefined colors, improving visual organization and user interaction. They are useful when you need to highlight status indicators, alerts, or navigation elements without moving to full-color graphics. This makes them a strong middle ground between monochrome simplicity and full-color TFT capability.
Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
Passive matrix LCDs use a simple structure that updates pixels row by row. This keeps cost and power consumption low, making them a smart choice for static or slow-moving content. Active matrix LCDs, such as those using TFT technology, control each pixel individually. This allows for faster refresh rates, sharper images, and smoother user experiences.
The decision depends on how dynamic the display content is. More complex visuals benefit from active matrix, while simpler interfaces can perform reliably with passive matrix designs.
Things to Consider
Focus on how the display will be used, what it needs to show, and where it will operate. Matching features to real-world use helps streamline development and improve product performance.
Personalizacja
Standard LCDs offer more flexibility for customization. They can be adapted to fit unique size, interface, and mounting needs without requiring a complete redesign. Newhaven Display provides custom support to help align display performance with your product goals.
Zastosowanie
TFTs are ideal for products that need higher resolution, brighter output, or interactive features. Standard LCDs are better suited for utilitarian applications where function, simplicity, and efficiency are the priority.
How You Plan to Drive the Display
Standard LCDs work well with lower-cost microcontrollers. They don’t require much power, speed, or memory. TFTs, on the other hand, need more capable hardware to handle higher data rates, color rendering, and screen refresh.
Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
Fact: Cost is driven by design, not just display type. While TFTs offer advanced features, a standard LCD with custom specs or added components can match or exceed that cost. The right choice depends on the product's specific needs and priorities.
Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
Fact: LCDs remain in high demand across industries. Newhaven Display continues to manufacture and supply a wide range of LCD options because they offer reliable performance, long product life, and cost efficiency. For designs that value stability, LCDs are still a smart and trusted choice.
Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
Fact: While standard LCDs tend to follow consistent industry formats, TFT displays often vary by manufacturer. Differences in interfaces, pinouts, and driver ICs are common. Understanding these variations early helps ensure a smoother design process. Newhaven Display works with teams to identify the right fit and avoid integration issues.
Wniosek
LCDs remain a reliable solution across a broad range of applications. Monochrome panels support efficiency and simplicity. TFT displays deliver vibrant visuals and greater interactivity. Understanding how each type functions, along with the differences between passive and active matrix technologies, ensures the display aligns with your product’s requirements.
To explore additional factors like viewing angles, brightness needs, or optical modes such as transmissive, transflective, and reflective, visit our LCD Types and Modes guide.
Get in touch with Newhaven Display to choose the right LCD panel for your application. We’re here to help with expert guidance and same-day quotes.


