Arten von LCD
15. September 2022
Flüssigkristallbildschirme (LCD) sind ein fester Bestandteil des Marktes für digitale Anzeigen und werden in allen Industriezweigen für Anzeigeanwendungen eingesetzt. Da jede Display-Anwendung einzigartige Anforderungen stellt, ist die Auswahl an spezialisierten LCDs gewachsen, um diese Anforderungen zu erfüllen.
LCD-Bildschirme können in drei Kategorien eingeteilt werden: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching) und VA (Vertical Alignment). Jeder dieser Bildschirmtypen hat seine eigenen einzigartigen Eigenschaften, die fast alle damit zu tun haben, wie die Bilder auf den verschiedenen Bildschirmtypen erscheinen.
In diesem Artikel:
- TN (Verdrehte Nematik)
- VA (Vertikale Ausrichtung)
- IPS (In-Plane-Switching)
- Vergleichstabelle TN vs. VA vs. IPS
- Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
- Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
- Things to Consider
- Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
- Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
- Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
- Schlussfolgerung
Verwandt: OLED vs. LCD
It's worth noting that although these screen types belong to the LCD screen type, they use thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology which is a variant of the standard LCD screen type.
Die Hauptunterscheidungsmerkmale von LCD-Bildschirmen sind Helligkeit, Betrachtungswinkel, Farbe und Kontrast.
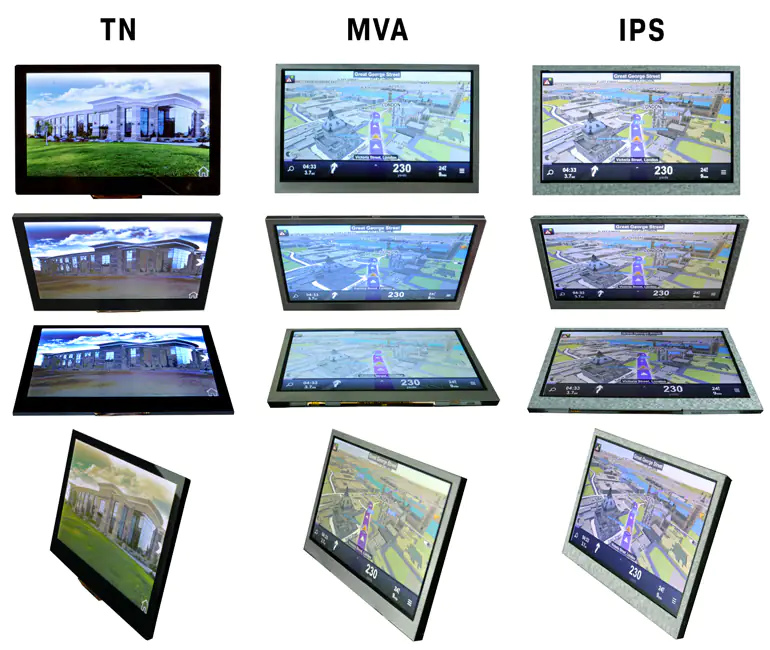
TN (Verdrehte Nematik)
Diese Technologie besteht aus nematischen Flüssigkristallen, die zwischen zwei Glasplatten eingebettet sind. Wenn Strom an die Elektroden angelegt wird, verdrehen sich die Flüssigkristalle um 90°. TN (Twisted Nematic)-LCDs sind der am häufigsten verwendete LCD-Bildschirmtyp. Sie bieten vollfarbige Bilder und moderate Betrachtungswinkel.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one, TN LCDs have faster response times and refresh rates than other TFT LCDs.
TN-TFTs sind nach wie vor sehr beliebt bei wettbewerbsorientierten PC-Spielen, bei denen Genauigkeit und Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit über Sieg oder Niederlage entscheiden können.
Aktualisierungsraten und Reaktionszeiten beziehen sich auf die Zeit, die Pixel benötigen, um sich als Reaktion auf Benutzereingaben zu aktivieren und zu deaktivieren; dies ist entscheidend für sich schnell bewegende Bilder oder Grafiken, die so schnell wie möglich und mit äußerster Präzision aktualisiert werden müssen.
TN-Displays sind aufgrund ihrer zuverlässigen Leistung und ihres kostengünstigen Preises nach wie vor beliebt.
TN LCD Eigenschaften

-
Kostengünstig
Gedrehte nematische Bildschirme sind traditionell die kostengünstigste LCD-Option.
-
Höchste Aktualisierungsraten
TN-LCD-Bildschirme haben die höchsten Bildwiederholraten und Reaktionszeiten.
-
Eingeschränkte Betrachtungswinkel
TN-LCD-Bildschirme haben einen durchschnittlichen Betrachtungswinkel von 45-65 Grad.
-
Begrenzte Helligkeit
TN-LCD-Bildschirme sind nicht hell genug für den Einsatz im Freien oder bei direkter Sonneneinstrahlung.
VA (Vertikale Ausrichtung)
VA-Displays, auch bekannt als Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment (MVA), bieten Funktionen, die sowohl bei TN- als auch bei IPS-Bildschirmen zu finden sind. Die Pixel in VA-Displays richten sich vertikal am Glassubstrat aus, wenn Spannung angelegt wird, und lassen Licht durch.
Displays mit VA-Bildschirmen bieten weite Betrachtungswinkel, hohen Kontrast und gute Farbwiedergabe. Sie haben eine ähnlich hohe Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit wie TN-TFTs, erreichen aber möglicherweise nicht die gleiche Helligkeit bei Sonnenlicht wie vergleichbare TN- oder IPS-LCDs. VA-Displays eignen sich in der Regel am besten für Anwendungen, die aus mehreren Blickwinkeln betrachtet werden müssen, wie z. B. digitale Beschilderungen in einem kommerziellen Umfeld.
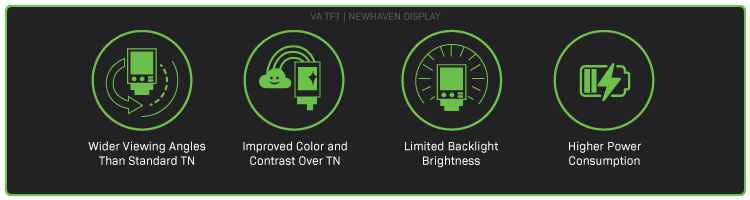
VA LCD Eigenschaften
-
Große Betrachtungswinkel
VA-Bildschirme bieten größere Betrachtungswinkel als TN-LCDs.
-
Farben und Kontraste
VA-LCD-Bildschirme haben im Vergleich zu TN-TFTs bessere Farben und einen besseren Kontrast.
-
Hintergrundbeleuchtung Helligkeit
VA-LCD-Bildschirme haben in der Regel eine geringere Helligkeit als ein entsprechendes TN-TFT-Modell.
-
Stromverbrauch
Sonnenlichtlesbare LCDs können mehr Energie verbrauchen als herkömmliche LCD-Bildschirme.
IPS (In-Plane-Switching)
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
Verwandt: Was ist ein IPS-Display?
IPS übertrifft TN-Displays in jeder wichtigen Kategorie.
IPS is superior in contrast, brightness, viewing angles, and color representation compared to TN screens. Images on screen retain their quality without becoming washed out or distorted, no matter what angle they’re viewed from. Because of this, viewers have the flexibility to view content on the screen from almost anywhere rather than having to look at the display from a front-center position.
IPS ermöglicht farbenfrohe, präzise und scharfe Bilder aus nahezu jedem Blickwinkel.
IPS-Displays bieten eine etwas niedrigere Bildwiederholfrequenz als TN-Displays. Denken Sie daran, dass die Zeit, in der die Pixel von inaktiv zu aktiv wechseln, in Millisekunden gemessen wird. Für die meisten Benutzer wird der Unterschied in der Bildwiederholfrequenz also unbemerkt bleiben.
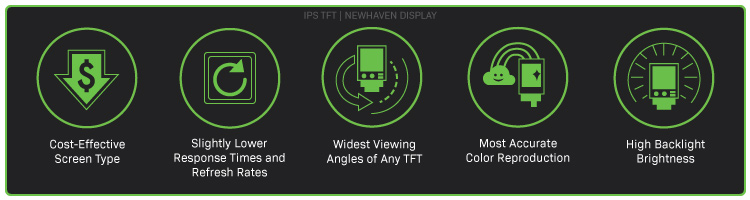
IPS-LCD-Eigenschaften
-
Preis Punkt
IPS-Displays sind jetzt kostengünstiger als TN-LCDs.
-
Durchschnittliche Aktualisierungsraten
IPS-Bildschirme haben langsamere Bildwiederholraten und Reaktionszeiten als TN-LCD-Bildschirme.
-
Größte Betrachtungswinkel
IPS-LCD-Bildschirme haben den größten Betrachtungswinkel unter den TFT-LCDs.
-
Beste Farben
IPS-LCD-Bildschirme erzeugen die genauesten und lebendigsten Farben aller TFT-LCDs.
-
Höchste Helligkeit
IPS-LCD-Bildschirme verfügen über eine helle Hintergrundbeleuchtung, so dass sie auch bei Sonnenlicht gut lesbar sind.
Vergleichstabelle TN vs. VA vs. IPS
| TN | VA | IPS | |
| Helligkeit | Besser | Gut | Am besten |
| Leistung | Schnellste | Schnell | Schnell |
| Betrachtungswinkel | Gut | Besser | Am besten |
| Farbe | Gut | Besser | Am besten |
| Kontrast | Gut | Am besten | Besser |
| Schwarzwerte | Gut | Am besten | Besser |
| Bildqualität | Gut | Besser | Am besten |
| Verwendet | Spielen wegen der Leistung | Allgemeine Verwendung aufgrund des Preises und der Qualität | Professionell, wo Qualität gefragt ist |
Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
Standard LCDs are ideal for straightforward applications where simplicity, longevity, and low power consumption are key. TFT LCDs deliver enhanced visuals and interactivity, making them better suited for versatility or graphic-rich interfaces. Choosing between them depends on your project’s design priorities, environment, and user needs.
Monochrome
Monochrome LCDs use one color for display content, typically black or blue on a light background. They are optimized for basic communication needs, offering strong visibility, extended product life, and efficient power use. These displays are a reliable fit for designs where function matters more than form.
Multi-Color
Multi-color LCDs display content in two or more predefined colors, improving visual organization and user interaction. They are useful when you need to highlight status indicators, alerts, or navigation elements without moving to full-color graphics. This makes them a strong middle ground between monochrome simplicity and full-color TFT capability.
Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
Passive matrix LCDs use a simple structure that updates pixels row by row. This keeps cost and power consumption low, making them a smart choice for static or slow-moving content. Active matrix LCDs, such as those using TFT technology, control each pixel individually. This allows for faster refresh rates, sharper images, and smoother user experiences.
The decision depends on how dynamic the display content is. More complex visuals benefit from active matrix, while simpler interfaces can perform reliably with passive matrix designs.
Things to Consider
Focus on how the display will be used, what it needs to show, and where it will operate. Matching features to real-world use helps streamline development and improve product performance.
Anpassung
Standard LCDs offer more flexibility for customization. They can be adapted to fit unique size, interface, and mounting needs without requiring a complete redesign. Newhaven Display provides custom support to help align display performance with your product goals.
Usage
TFTs are ideal for products that need higher resolution, brighter output, or interactive features. Standard LCDs are better suited for utilitarian applications where function, simplicity, and efficiency are the priority.
How You Plan to Drive the Display
Standard LCDs work well with lower-cost microcontrollers. They don’t require much power, speed, or memory. TFTs, on the other hand, need more capable hardware to handle higher data rates, color rendering, and screen refresh.
Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
Fact: Cost is driven by design, not just display type. While TFTs offer advanced features, a standard LCD with custom specs or added components can match or exceed that cost. The right choice depends on the product's specific needs and priorities.
Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
Fact: LCDs remain in high demand across industries. Newhaven Display continues to manufacture and supply a wide range of LCD options because they offer reliable performance, long product life, and cost efficiency. For designs that value stability, LCDs are still a smart and trusted choice.
Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
Fact: While standard LCDs tend to follow consistent industry formats, TFT displays often vary by manufacturer. Differences in interfaces, pinouts, and driver ICs are common. Understanding these variations early helps ensure a smoother design process. Newhaven Display works with teams to identify the right fit and avoid integration issues.
Schlussfolgerung
LCDs remain a reliable solution across a broad range of applications. Monochrome panels support efficiency and simplicity. TFT displays deliver vibrant visuals and greater interactivity. Understanding how each type functions, along with the differences between passive and active matrix technologies, ensures the display aligns with your product’s requirements.
To explore additional factors like viewing angles, brightness needs, or optical modes such as transmissive, transflective, and reflective, visit our LCD Types and Modes guide.
Get in touch with Newhaven Display to choose the right LCD panel for your application. We’re here to help with expert guidance and same-day quotes.


