Transmissive vs Reflective vs Transflective Displays
Jan 31st 2023
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) are widely used in electronic devices for all kinds of industries. They are typically divided into three display types based on their light transmission modes. The three main types of LCD modes are transmissive, reflective, and transflective. The main difference is how they use light to illuminate the pixels in the display.
Types of LCD modes:
- Transmissive LCDs require a backlight for clear visibility.
- Reflective LCDs do not have a backlight and rely on external light sources.
- Transflective LCDs combine both transmissive and reflective properties.
Each display mode has its own advantages and disadvantages related to the available lighting conditions and the application's environment.
Related: Nits vs Lumens vs Luminance
In this article:
Transmissive LCD displays
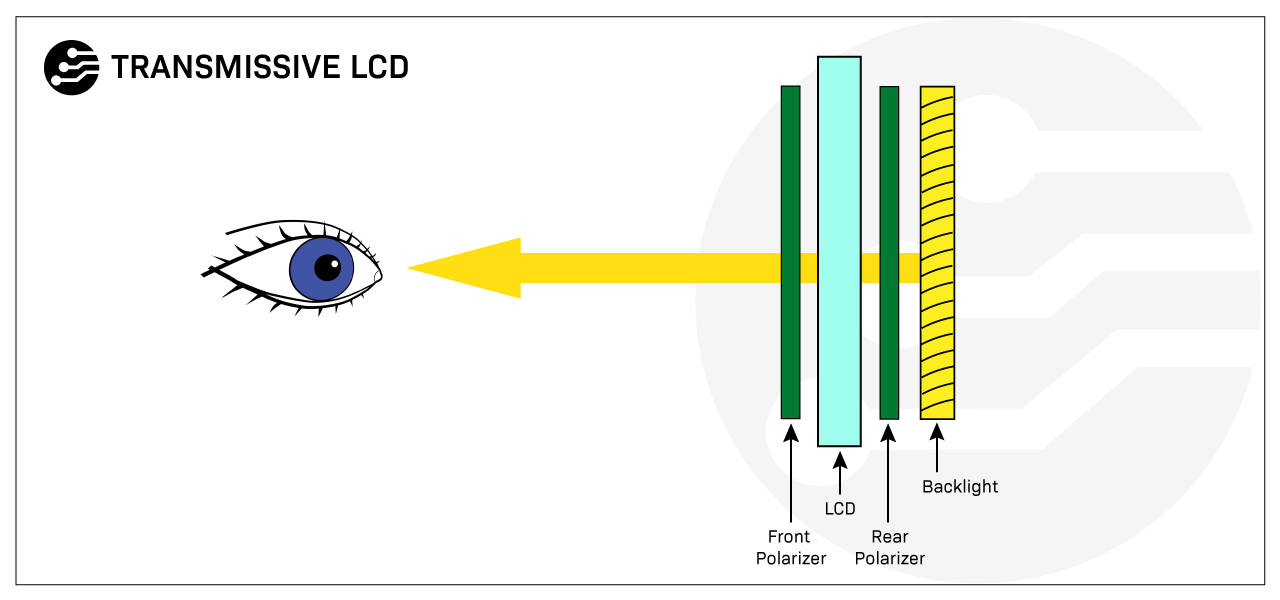
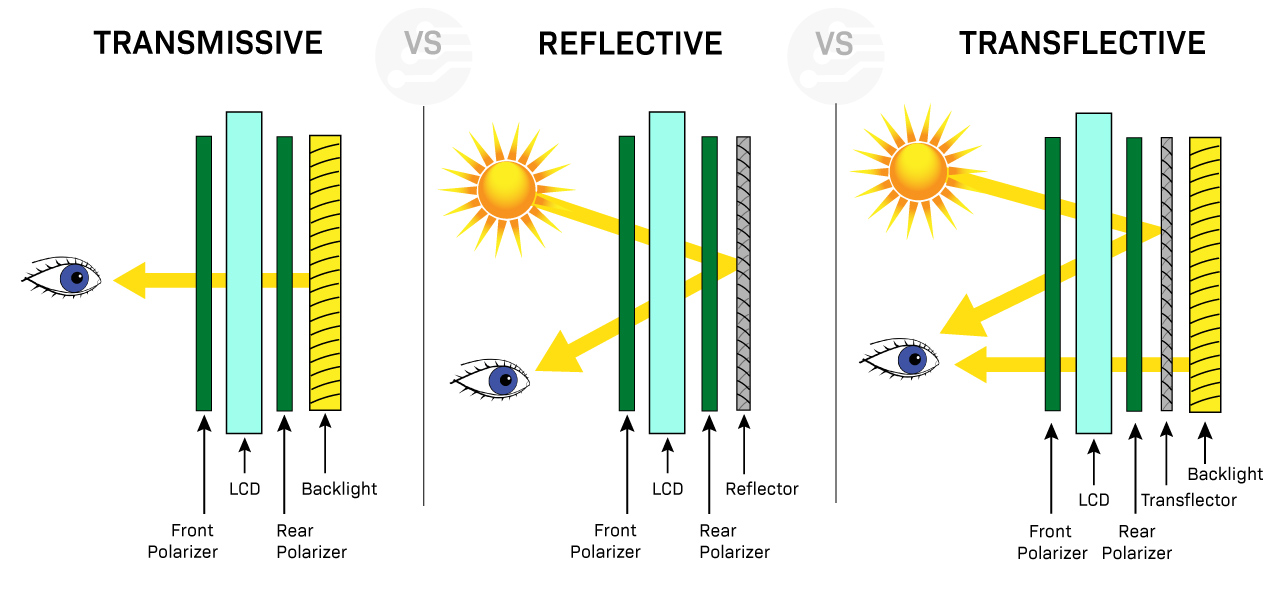
Transmissive displays rely on a backlight to be visible. For this kind of display, light emitting from the back of the display glass must pass through the LCD towards the front to light the pixels. Transmissive LCDs are suitable in low-light environments since they rely on a backlight to be visible. These displays are also used in applications where high-resolution images, videos, and high quality are important, which is why you will commonly find TFT displays with a transmissive display mode.
Related: Types of LCD comparison: TN vs VA vs IPS
How do transmissive displays work?
Transmissive displays work by transmitting light through the surface of the display. This is achieved by using a series of layers, including a layer of liquid crystal that can be manipulated to control the amount of light passing through, a backlight to provide the light source and an outer layer of protective glass or plastic. When an electrical current is applied to a pixel in the display, it allows more or less light to pass through, creating an image.
Transmissive LCD uses
The most common devices using transmissive LCDs are smartphones, tablets, computer monitors, and televisions. They are also used in digital cameras, camcorders, automotive displays, navigation systems, in-flight entertainment systems, medical equipment, kiosks, and point-of-sale (POS) terminals.
You can also find transmissive display modes in graphic LCDs, and character LCDs with negative display types creating bright light pixels on blue or dark backgrounds.
Advantages of transmissive LCDs
- High image quality: Transmissive LCDs can produce high-quality, bright, vivid images with a wide color gamut and high contrast ratio.
- Good visibility in low-light environments: Transmissive LCDs rely on a backlight to be visible, which makes them suitable for darker lighting conditions.
- Wide viewing angles: Transmissive LCDs have wide viewing angles, making viewing the display from various positions easy.
- Suitable for high-resolution: Transmissive LCDs can handle high-resolution images and videos.
Disadvantages of transmissive LCDs
- High power consumption: Transmissive LCDs require a backlight to be visible, which increases power consumption and reduces the end product's battery life.
- Reduced visibility in bright sunlight: Transmissive LCDs are not well-suited for use in direct sunlight, as the backlight can wash out the display.
- Susceptible to glare: Transmissive LCDs can be affected by glare, making it difficult to view the display in certain lighting conditions.
Related: Types Of LCDs
Reflective LCD displays
Reflective displays rely on bright ambient light to be visible. There is no backlight source inside this kind of display; instead, light is reflected from the surrounding environment for the pixels to be visible.
How do reflective displays work?
Reflective LCDs work by using a reflective layer along with the polarizing filter, to reflect the light back to the user's eyes instead of emitting light from a backlight. The liquid crystal layer modulates the amount of light that is reflected back, creating the desired image.

Reflective LCD uses
Reflective LCDs are great for outdoor or sunlight-readable applications where the device is exposed to direct sunlight. These displays are also used in small handheld devices where power consumption is a concern.
You can also find reflective display modes in graphic COG LCDs and character LCDs with positive display types. The most common devices using reflective LCDs are outdoor applications such as GPS devices and portable devices such as e-readers, camera viewfinders, and digital watches.
Advantages of reflective LCDs
- Low power consumption: Reflective LCDs do not require a backlight, which reduces their power consumption and extends the device's battery life.
- High visibility in sunlight: The reflective nature of the display allows it to be easily read in bright sunlight.
- Thin and lightweight: Reflective LCDs are thinner and lighter than transmissive LCDs since they don't have a backlight, making them well-suited for portable devices.
Disadvantages of reflective LCDs
- Limited viewing angles: Reflective LCDs have a limited viewing angle, making it difficult to read the display from certain angles.
- Poor performance in low light: Reflective LCDs are not well-suited for low-light environments, as they rely on bright ambient light to be visible.
- Reduced color depth: Reflective LCDs typically have a reduced color depth compared to transmissive LCDs, which can affect the overall image quality.
Transflective LCD displays
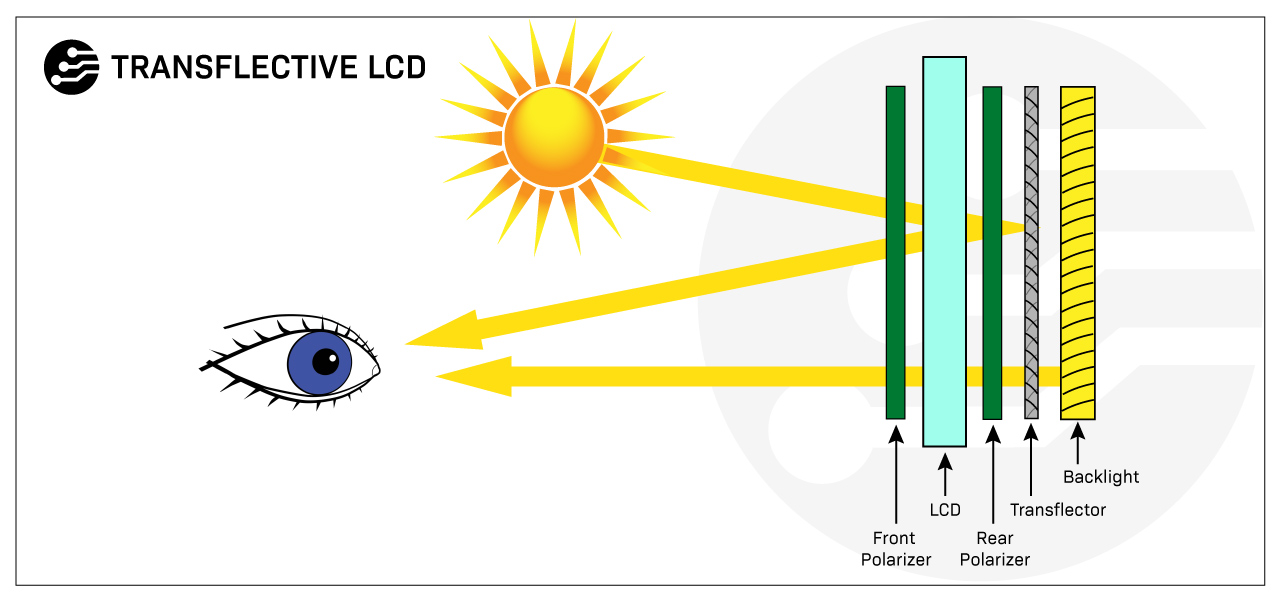
Transflective displays combine backlighting and ambient light reflection to illuminate the pixels, resulting in a display with both transmissive and reflective properties.
How do transflective LCDs work?
In a transflective LCD, a backlight is used to illuminate the screen in low-light conditions, such as indoors or at night. In bright light conditions, such as outdoors or direct sunlight, the screen can be viewed by reflecting ambient light off the surface of the LCD.
Transflective LCD uses
Transflective LCDs are commonly used in industrial and medical equipment, where it's essential to have high visibility in any lighting conditions. They are also widely used in marine, military, and aviation applications where the operator needs to see the display in bright and low light conditions.
Advantages of transflective LCDs
- High visibility and contrast: Transflective LCDs combine the benefits of reflective and transmissive displays, providing good visibility in both bright sunlight and low-light environments.
- Low power consumption: Transflective LCDs do not require a backlight always on, which reduces power consumption and extends battery life when the backlight is off.
- Wide viewing angles: Transflective LCDs have wider viewing angles than reflective LCDs.
Disadvantages of transflective LCDs
- Limited color depth: Transflective LCDs typically have a reduced color depth compared to transmissive LCDs, which can affect overall image quality.
Related: OLEDs vs LCDs
Conclusion
In summary, transmissive LCDs are for low-light use, reflective LCDs are for bright-light use, and transflective LCDs work well in both environments. Transmissive displays will continue to be used in applications where high-quality images and videos are required, such as televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones. Reflective displays will continue to be used in applications where power consumption is a concern, such as in e-readers, small handheld devices, and outdoor applications. Transflective displays are expected to be used in more portable devices and applications where visibility in changing lighting conditions is essential, such as in medical equipment, industrial, marine, and aviation applications.
The future of transmissive, reflective, and transflective LCD displays is likely to be influenced by technological advances and changes in consumer preferences. LCDs may eventually be replaced by newer technologies such as OLEDs, Micro-LEDs, and QD-LCDs. For now, LCDs are still a widely used display technology, with display types and modes equipped for every kind of industry and environment.