画面焼き付きとは何か?なぜ発生するのか?
2022年8月5日
画像焼き付きは、携帯電話、モニター、ウェアラブル機器、テレビ、ディスプレイ画面を持つすべての電子機器のLCDや OLEDを含む、すべての画面ディスプレイに影響を与える。この記事では、画像焼き付きについて知っておくべきこと、そして画像焼き付きを軽減する方法について解説する。
この記事で学べることは以下の通りです。
画面の焼き付きとは?
画面の焼き付きは、焼き付きとも呼ばれ、ディスプレイ上に永続的なゴーストのような痕跡が残ることで起こります。この問題は 有機EL(有機発光ダイオード)ディスプレイに最もよく関連する、 LCD(液晶ディスプレイ)でも、イメージ・パーシステンスと呼ばれる一時的な画像保持が発生することがある。異なるディスプレイ技術が長時間の静止画像にどのように反応するかを理解することは、産業、医療、商業環境でのアプリケーションを設計するエンジニアにとって極めて重要である。
関連情報静電気放電(ESD)とは
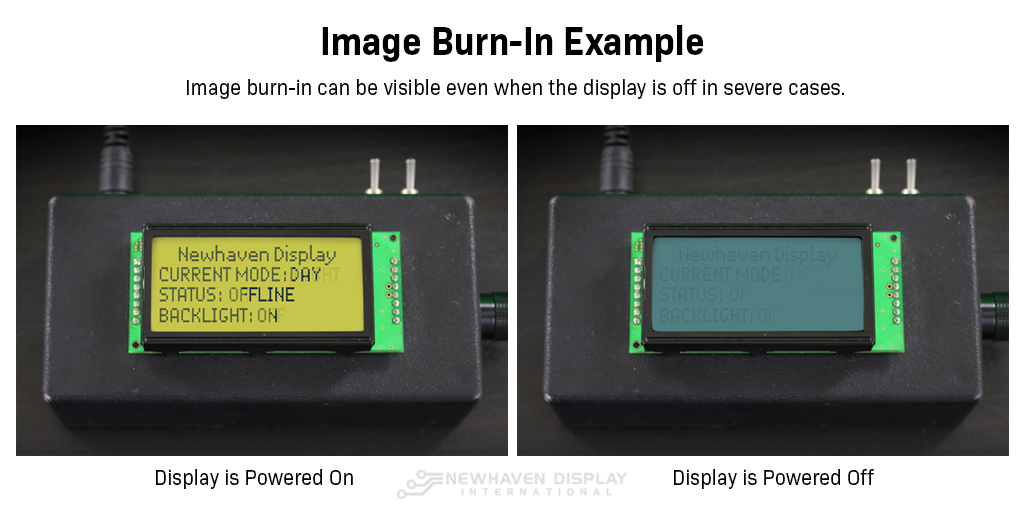 液晶ディスプレイの画像焼き付き例。
液晶ディスプレイの画像焼き付き例。
バーンインとイメージリテンション
画像焼き付きと画像保持に遭遇したことはあるだろうが、どちらかわからなかったはずだ。どちらも同じような視覚効果があるため、間違えやすいのですが、1つだけ重要な違いがあります:画像保持は一時的なもので、画像焼きつきは永久的なものです。
私たちは、画像の焼き付きを「修正」したり、ディスプレイから画像焼き付きを除去したりすることについて、多くの誤解を招く記事やビデオ、ガイドを目にしてきました。画像の焼き付きは、一度ディスプレイの画面に発生すると、完全に元に戻りません。
ほとんどの場合、これらのガイドでは、画像保持の仕組みとその回復プロセスを加速する方法について説明しています。液晶ディスプレイや有機ELディスプレイの画像焼き付きと画像保持について、皆さんが抱いている疑問を解消したいと思います。
画像保持
ゴーストや画像持続性とも呼ばれる画像保持は、液晶ディスプレイや有機ELディスプレイで、通常数秒の短時間だけ画像が見えるようになる一時的な効果である。
画像保持と画面の焼きつきを見分けるには?
短時間で画像が消えてしまう場合は、一時的な画像保持に対処していることになります。画像が永久に残る場合は、画像の焼き付きに対処しています。
画像の保持は、それを消すためにユーザーが介入する必要はありません。TFTや新しいIPSディスプレイのような新しいディスプレイ技術では、焼き付きが発生する前に画像保持が発生することがよくあります。
関連記事 IPSディスプレイって何?
画像の保持は薄れますが、そのプロセスを早めるために使えるヒントがいくつかあります。スクリーンセーバーを使う、画面上のさまざまなグラフィックを循環させてピクセルを動かす、可能な限りディスプレイの電源を切る、といった簡単な行動が、ディスプレイの画像保持をクリアするのに役立ちます。
これらは、画像焼けの「治療法」として宣伝されているものと同じですが、騙されないでください。焼きつきは治りませんが、焼きつきを防ぐ方法だけはあります。
画面が焼き付き損傷していると判断する前に、以下のヒントを試して、単なる画像保持かどうかを確認するのをお待ちください。画像の保持は無害であり、多くのスクリーンでよく見られる現象です。
画面の焼き付きの原因は?
画面の焼きつきは、画面のピクセルが長時間、静止した状態で活性化し続けることによって起こります。 ロビーや待合室にあるテレビが、いつも同じニュースチャンネルを流していることを思い浮かべてほしい。チャンネルを変えても、ニュースチャンネルのフッターとロゴが画面に永久に焼きついてしまうのです。
ディスプレイの焼き付きの原因としては、静止画像、メッセージ、ロゴ、アイコンなどがよく挙げられます。
例えば携帯電話では、バッテリーやWifi、サービス信号のアイコンが常に静止していることが、画像の焼き付きを引き起こすことがあります。
LCDやOLEDの画素が一定の位置で活性化したままだと、やがてその位置で「動かなく」なってしまいます。そうすると、画面上に色あせた頑固なイメージが残ることになります。
液晶・有機ELディスプレイの焼き付きについて
焼き付きの結果はどの画面でも同じように見えるが、液晶と有機ELでは発生方法が少し異なる。
関連記事 有機ELと液晶の違い
液晶ディスプレイの焼き付きが発生する仕組み
静止画像を長時間表示していると、液晶ディスプレイの結晶の動きが弱くなり、完全に「ON」の状態から「OFF」の状態にすることが難しくなります
画素の活性化、非活性化に失敗すると、画面から消えない色あせた画像になる。これは、英数字の更新頻度が低いキャラクタLCDを使用するアプリケーションでよく見られる現象である。
下の例では、ディスプレイの電源を切った後、液晶画面に残った文字が色あせて永久に残っているのがわかると思います。
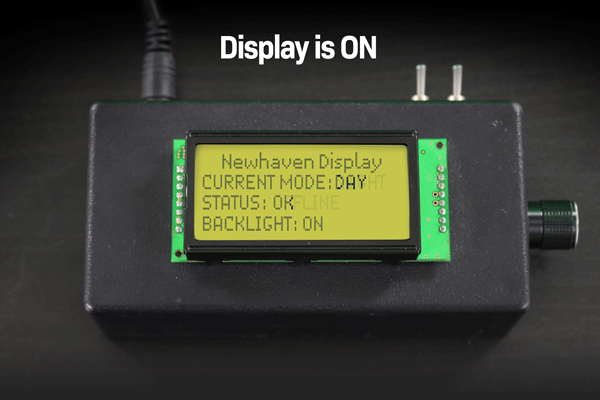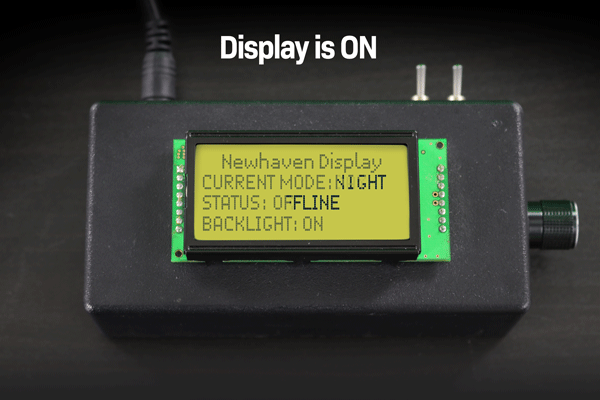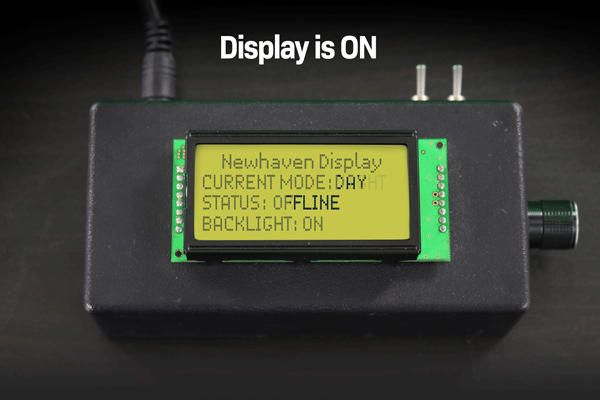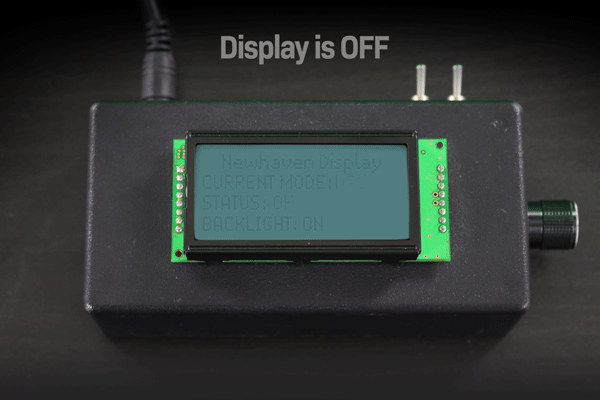 表示ON/OFF時の文字液晶画像焼き付き例。
表示ON/OFF時の文字液晶画像焼き付き例。
有機ELの焼き付きが発生する仕組み
有機ELの特徴は、バックライトを使わなくても点灯することです。ディスプレイの各画素は自発光型LEDなので、自分で光を発生させるのです。しかし、画素は時間が経つとどうしても明るさが失われてしまいます。有機ELの画素は、点灯している時間が長いほど、あまり使われていない画素の隣で薄暗く見えるようになります。
有機ELディスプレイでは、静止画を長く表示していると、全く違うものを表示しても、画素が前の画像の後ろに影を残してしまいます。
下の例では、「ダブルハイト」の文字が有機ELに焼き付けられている様子をご覧ください。
 有機EL画像の焼き付き例。
有機EL画像の焼き付き例。
覚えておいてください。焼き付きが発生してから除去したり、軽減したりする方法はありません。長時間、あるいはディスプレイを再起動しても頑固な画像が消えない場合は、画像の焼き付きが発生している可能性があります。
液晶画面焼けの初期症状
LCDはOLEDのような永久的な焼き付きに悩まされることはないが、イメージ・パーシスタンスと呼ばれる一時的な焼き付きが発生することがある。これは、表示内容が変わった後でも、静止画像がディスプレイ上にかすかに残る現象である。以下に、注意すべき初期の兆候を示す:
-
ゴーストまたは以前の画像のかすかな残り:画面を切り替えても、メニューバーやロゴ、その他の静的コンテンツの影が見える場合は、画像が残っている証拠です。
-
画像移行時の応答時間が遅い:ピクセルのリフレッシュや新しいコンテンツへの適応に時間がかかる場合、特にコントラストの高い領域では、LCDに初期の画像持続性が発生している可能性があります。
-
影響を受けた部分の色の歪み:静的コンテンツに長時間さらされると、ディスプレイの一部がわずかに変色したり、「ウォッシュアウト」して見えることがあります。
-
LCDのタイプによる違い:広視野角でよく使われるIPS(In-Plane Switching)パネルは、TN(Twisted Nematic)パネルよりも残像が出にくく、応答速度は速いがわずかな残像が出ることがある。
早期に発見された場合、ディスプレイの電源を切るか、ディスプレイのリフレッシュ機能を使うことで、画像の残存を元に戻すことができる。しかし、静的なコンテンツに長時間さらされると、より頑固な残存のリスクが高まる。
焼き付きやすいLCDアプリケーション
LCDはOLEDよりも永久的な焼き付きに弱いが、特定の産業では静止画像を頻繁に表示するディスプレイを使用しているため、画像の持続性が高くなりやすい。
-
医療機器のディスプレイ患者監視システム、診断画面、画像装置は、静的なバイタルサイン、グラフ、インターフェース要素を長時間表示することが多く、画像が保持される可能性が高くなります。
-
産業用制御パネル:ファクトリーオートメーションの画面、プロセス制御モニター、計装パネルは、読み出しやシステムステータスなどの静的データを長時間表示します。
-
POSシステム:小売店のレジディスプレイやキオスク端末では、同じユーザーインターフェイスが何時間も表示されることが多いため、ピクセルの磨耗が不均一になります。
-
自動車および船舶用ディスプレイ:ナビゲーション・システム、ダッシュボード表示、インフォテインメント・スクリーンは、同じ地図や計器のインターフェイスを長時間保持することがあり、一時的な保持を引き起こすことがあります。
-
テストおよび測定装置:オシロスコープ、スペクトラム・アナライザー、その他の実験用機器は、固定されたグラフィック・エレメントを備えていることが多く、長期間にわたって画像が持続する可能性があります。
ニューヘブンディスプレイの TFT LCDモジュールは、ピクセルシフト技術、最適化された輝度制御、および高度なリフレッシュ技術により設計されており、画像の保持を最小限に抑えます。これらの設計強化により、ミッションクリティカルな用途におけるディスプレイの寿命と信頼性が延びます。
OLEDスクリーン焼けの初期症状
LCDとは異なり、OLEDディスプレイは自己発光ピクセルのため、永久的な焼き付きに対してより脆弱である。このプロセスを加速させる条件を理解することは、長寿命製品を設計するエンジニアにとって不可欠である。OLEDバーンインの兆候には以下のようなものがある:
-
永続的なゴースト画像:ロゴやユーザーインターフェース(UI)コンポーネントなどの静的要素が、ディスプレイを切り替えても表示されたままである。
-
不均一な輝度レベル:画素の経年劣化(一部の画素が他の画素より早く劣化する)により、頻繁に使用する部分が暗く見えることがあります。
-
色の変化や歪み:影響を受けた領域は、焼き付きが発生した赤味、黄味、青味などの色の不均衡が発生することがあります。
-
高コントラスト領域で顕著な差異:焼き付きは、明るい要素が暗い背景の上に重なることが多く、輝度ムラが発生する場所で最も顕著に現れます。
燃えやすいOLEDアプリケーション
OLEDディスプレイは鮮やかな色と高いコントラストを提供し、多くの用途に理想的です。しかし、特定の用途では焼き付きの可能性が高くなります:
-
医療・診断用ディスプレイ 患者監視システムや画像機器は、静的な読み取り値やグラフィック要素を維持することがよくあります。
-
産業およびオートメーション・インターフェース:工場の制御ディスプレイには、永続的なナビゲーションメニューやシステムステータスが頻繁に表示されます。
-
ハンドヘルド機器とポータブル機器:OLEDベースのテスト機器、通信機器、特殊ツールは、静的なUIコンポーネントを表示することが多い。
-
自動車および航空宇宙用ディスプレイ:デジタルダッシュボード、ヘッドアップディスプレイ(HUD)、機内エンターテイメントスクリーンでは、固定ナビゲーション要素やブランディングが維持されます。
-
小売店や商業施設の看板:静的なロゴ、価格、宣伝用のグラフィックを特徴とするOLED広告ディスプレイはリスクが高い。
OLEDのバーンインを軽減するために、Newhaven DisplayはOLEDモジュールを設計しています。 OLEDモジュールを設計しています。ピクセルウェアレベリング、自動輝度調整、および内蔵ディスプレイリフレッシュサイクルを備えています。これらの機能は、高コントラストアプリケーションで使用されるOLEDディスプレイの動作寿命を延ばすのに役立ちます。
画面焼けをテストする方法
画面の焼き付きを早期に検出することで、画素のさらなる劣化を防ぐことができます。ここでは、LCDおよびOLEDディスプレイの画面焼けをテストする方法をいくつか紹介する:
-
フルスクリーン・カラーテスト:白、赤、緑、青などの無地の背景をフル輝度で表示すると、ゴースト画像やピクセルの不均一な磨耗が明らかになることがあります。
-
グラデーションとグレーのスクリーンテスト:グラデーションパターンや均一なグレーの背景を表示することで、微妙な色のずれを検出することができます。
-
高コントラスト画像間の切り替え:明るい画像と暗い画像を素早く交互に表示すると、特にディスプレイの使用頻度の高い部分で焼き付きが目立つことがあります。
-
専用のバーンインテストツールの使用診断アプリケーションの中には、持続的な画像保持やOLEDバーンインを強調するように設計されたテストパターンを生成するものがあります。
軽度の画像保持が検出された場合、ピクセル・リフレッシュ・サイクルを実行したり、輝度レベルを調整したり、スクリーンセーバーを使用したりすることで、視認性を低下させることができる。しかし、OLEDディスプレイの永久的な焼き付きは元に戻すことができないため、予防的な対策が最善の方法となる。
画面の焼き付きを軽減/回避する方法
どんなに高性能なディスプレイでも、いつかは焼き付きが発生します。しかし、焼き付きが発生する前に、画面の寿命を延ばすためにできる簡単な対処法がいくつかあるのです。適切な方法で対処すれば、焼き付き現象のない優れた性能を何年も発揮させることができます。
画面の焼き付きを防ぐには
- 未使用時のディスプレイの電源オフ
- スクリーンセーバーを利用する
- ピクセルを動かす(回転またはスクロール効果)
- 画面の輝度またはコントラストを下げる
関連項目 電子ディスプレイのクリーニング方法
ご存じですか?スクリーンセーバーの名前の由来は、本来の目的である画面の焼き付きを軽減するための能動的な方法であったからです。
未使用時のディスプレイの電源オフ
ディスプレイを常時点灯させる必要がある場合や、ディスプレイを長時間点灯させる必要がある場合があることは承知しています。
もし機会があれば、ディスプレイの電源を完全に入れ直すことをお勧めします。これにより、画素がリセットされ、焼き付きを防ぐことができます。
パワーサイクルがオプションでない場合、ディスプレイのON/OFFコマンドを使用して、ディスプレイをオフにすることができます。また、RAMに表示データを保持したまま、ディスプレイをスリープモードにすることも可能です。
スクリーンセーバーを利用する
ディスプレイの電源を切ることができない場合は、スクリーンセーバーを利用するとよいでしょう。常時ONにする必要がないディスプレイの場合、使用していないときは画面を休ませておくと便利です。
スクリーンセーバーやスリープモードにすると、電源を完全に切ってからもう一度入れるのに比べ、素早く起動することができます。
画素を動かす
画素を動かせ!ピクセルは固定されている時間が長いほど、焼きつきに近づきます。テキストをスクロールさせたり、画像を動かしたり、色を変えたりして、スクリーンのピクセルを動かすことができます。
このテクニックは、車のタイヤをローテーションさせるのと同じです。目標は、ディスプレイ全体の摩耗を均等に分散させることです。
画面の輝度またはコントラストを下げる
画面の明るさはできるだけ抑える照度(明るさ)を上げると、より多くの電流が必要となり、LEDの寿命が短くなります。
有機ELディスプレイの場合、コントラストを下げると輝度が下がり、画像の焼き付きが少なくなる。照度(明るさ)を上げると、より多くの電流が必要となり、有機ELの画素の寿命が短くなる。
液晶ディスプレイの場合、コントラストを下げると液晶への負担が少なくなり、画素が弱くなったり、固まったりする割合が少なくなります。
液晶と有機ELの焼き付きについてのすべて - [動画]を見る
私たちのYouTubeチャンネルで、このような役に立つビデオをもっとご覧ください。
結論
画像の焼き付きは元に戻すことができず、一度発生すると直すことができないことを忘れないでください。スクロール効果、画素の回転、スクリーンセーバーの使用、未使用時の画面オフなど、ディスプレイの寿命を延ばすためには、画像の焼き付き防止策を確立することが不可欠です。