Tipi di LCD
15 settembre 2022
Gli schermi a cristalli liquidi (LCD) sono un punto fermo nel mercato dei display digitali e vengono utilizzati in applicazioni di visualizzazione in tutti i settori. Poiché ogni applicazione di visualizzazione presenta una serie di requisiti unici, la selezione di LCD specializzati è cresciuta per soddisfare queste esigenze.
Gli schermi LCD possono essere raggruppati in tre categorie: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching) e VA (Vertical Alignment). Ognuno di questi tipi di schermo ha le sue qualità uniche, quasi tutte legate al modo in cui le immagini vengono visualizzate sui vari tipi di schermo.
In questo articolo:
- TN (Nematico Contorto)
- VA (Allineamento verticale)
- IPS (commutazione in piano)
- Tabella di confronto tra TN e VA e IPS
- LCD standard vs LCD TFT
- LCD a matrice passiva vs LCD a matrice attiva
- Cose da considerare
- Mito: i display TFT sono sempre più costosi dei display LCD standard
- Mito: l'LCD è una tecnologia obsoleta e in via di dismissione
- Mito: tutti gli schermi LCD seguono gli standard industriali
- Conclusione
Correlato: OLED vs LCD
Vale la pena notare che, sebbene questi tipi di schermo appartengano alla categoria degli schermi LCD, utilizzano la tecnologia a transistor a film sottile (TFT), che è una variante dello schermo LCD standard.
Le caratteristiche principali che differenziano i tipi di schermo LCD sono la luminosità, gli angoli di visione, il colore e il contrasto.
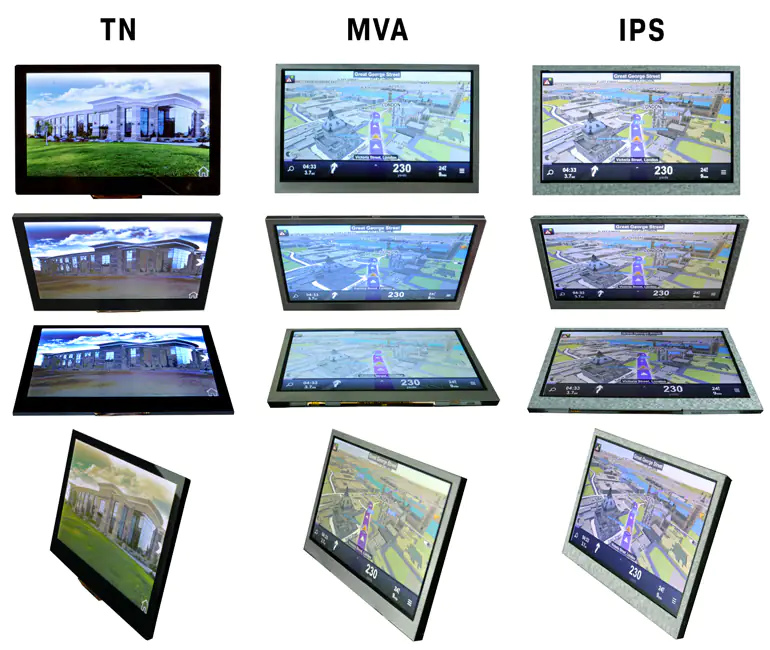
TN (Nematico Contorto)
Questa tecnologia consiste in cristalli liquidi nematici inseriti tra due lastre di vetro. Quando l'alimentazione viene applicata agli elettrodi, i cristalli liquidi si attorcigliano di 90°. Gli LCD TN (Twisted Nematic) sono il tipo di schermo LCD più comune. Offrono immagini a colori e angoli di visione moderati.
Gli schermi LCD TN mantengono una base di utenti fedeli nonostante la crescente popolarità di altri tipi di schermi, grazie ad alcune caratteristiche chiave uniche offerte dai display TN. Innanzitutto, gli schermi LCD TN hanno tempi di risposta e frequenze di aggiornamento più rapidi rispetto agli altri schermi LCD TFT.
I TFT TN rimangono molto popolari tra le comunità di giocatori di PC competitivi, dove la precisione e la velocità di risposta possono fare la differenza tra la vittoria e la sconfitta.
La velocità di aggiornamento e i tempi di risposta si riferiscono al tempo necessario ai pixel per attivarsi e disattivarsi in risposta agli input dell'utente; si tratta di un fattore cruciale per le immagini in rapido movimento o per la grafica che deve aggiornarsi il più rapidamente possibile con estrema precisione.
I display TN rimangono popolari grazie alle loro prestazioni affidabili e al prezzo conveniente.
Caratteristiche del display LCD TN

-
Economicamente vantaggioso
Gli schermi nematici ritorti rappresentano tradizionalmente l'opzione LCD più conveniente.
-
Tassi di aggiornamento più elevati
Gli schermi LCD TN hanno le frequenze di aggiornamento e i tempi di risposta più elevati.
-
Angoli di visione limitati
Gli schermi LCD TN hanno angoli di visione medi di 45-65 gradi.
-
Luminosità limitata
Gli schermi LCD TN non sono sufficientemente luminosi per la visione all'aperto o alla luce diretta del sole.
VA (Allineamento verticale)
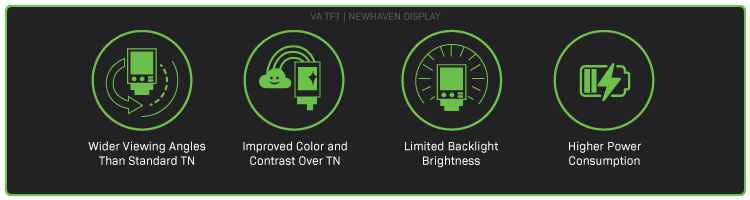
I display VA, noti anche come MVA ( Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment ), offrono caratteristiche presenti sia negli schermi TN che in quelli IPS. I pixel dei display VA si allineano verticalmente al substrato di vetro quando viene applicata la tensione, consentendo il passaggio della luce.
I display con schermi VA offrono ampi angoli di visione, contrasto elevato e buona riproduzione dei colori. Mantengono un'elevata velocità di risposta, simile a quella dei TFT TN, ma potrebbero non raggiungere gli stessi livelli di luminosità leggibili alla luce del sole degli LCD TN o IPS. I display VA sono generalmente più indicati per le applicazioni che devono essere visualizzate da più angolazioni, come la segnaletica digitale in ambito commerciale.
Caratteristiche del display LCD VA
-
Ampi angoli di visione
Gli schermi VA offrono angoli di visione più ampi rispetto agli LCD TN.
-
Colori e contrasto
Gli schermi LCD VA presentano colori e contrasto migliori rispetto ai TFT TN.
-
Luminosità della retroilluminazione
Gli schermi LCD VA tendono a offrire una luminosità inferiore rispetto a un modello TFT TN equivalente.
-
Consumo di energia
Gli LCD leggibili alla luce del sole possono consumare più energia degli schermi LCD standard.
IPS (commutazione in piano)
La tecnologia IPS (In-Plane Switching) migliora la qualità dell'immagine agendo sui cristalli liquidi all'interno dello schermo. Quando viene applicata la tensione, i cristalli ruotano parallelamente (o "in piano") anziché verticalmente, consentendo il passaggio della luce. Questo comportamento comporta diversi miglioramenti significativi alla qualità dell'immagine di questi schermi.
Correlato: Che cos'è un display IPS?
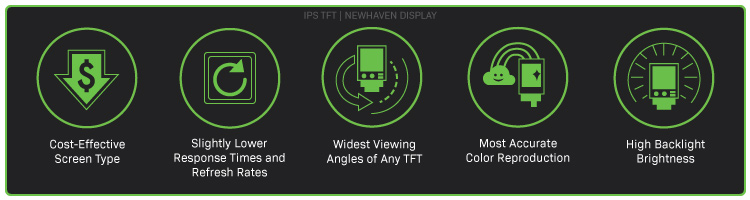
I display IPS superano quelli TN in tutte le principali categorie.
Rispetto agli schermi TN, gli schermi IPS offrono prestazioni superiori in termini di contrasto, luminosità, angoli di visione e resa dei colori. Le immagini sullo schermo mantengono la loro qualità senza sbiadire o distorcersi, indipendentemente dall'angolo di visione. Ciò consente agli spettatori di guardare i contenuti sullo schermo da quasi qualsiasi posizione, senza doversi necessariamente sedere davanti al display.
L'IPS consente di ottenere immagini colorate, precise e nitide viste da quasi tutte le angolazioni.
I display IPS offrono una frequenza di aggiornamento leggermente inferiore rispetto ai display TN. Ricordiamo che il tempo di passaggio dei pixel da inattivi ad attivi si misura in millisecondi. Pertanto, per la maggior parte degli utenti, la differenza di frequenza di aggiornamento passerà inosservata.
Caratteristiche del display LCD IPS
-
Punto prezzo
I display IPS sono ora più convenienti rispetto agli LCD TN.
-
Tassi medi di aggiornamento
Gli schermi IPS hanno frequenze di aggiornamento e tempi di risposta più lenti rispetto agli schermi LCD TN.
-
Angoli di visione più ampi
Gli schermi LCD IPS hanno gli angoli di visione più ampi di tutti gli LCD TFT.
-
I migliori colori
Gli schermi LCD IPS producono i colori più precisi e vividi di tutti gli LCD TFT.
-
Massima luminosità
Gli schermi LCD IPS sono dotati di retroilluminazione ad alta luminosità per ambienti leggibili alla luce del sole.
Tabella di confronto tra TN e VA e IPS
| TN | VA | IPS | |
| Luminosità | Meglio | Buono | Il meglio |
| Prestazioni | Il più veloce | Veloce | Veloce |
| Angolo di visione | Buono | Meglio | Il meglio |
| Colore | Buono | Meglio | Il meglio |
| Contrasto | Buono | Il meglio | Meglio |
| Livelli di nero | Buono | Il meglio | Meglio |
| Qualità dell'immagine | Buono | Meglio | Il meglio |
| Utilizzi | Gioco per le prestazioni | Uso generale per prezzo e qualità | Professionale dove è richiesta la qualità |
LCD standard vs LCD TFT
Gli LCD standard sono ideali per applicazioni semplici in cui sono fondamentali la semplicità, la longevità e il basso consumo energetico. Gli LCD TFT offrono immagini e interattività migliorate, rendendoli più adatti alla versatilità o alle interfacce ricche di grafica. La scelta tra i due tipi dipende dalle priorità di progettazione del progetto, dall'ambiente e dalle esigenze degli utenti.
Monocromatico
Gli LCD monocromatici utilizzano un solo colore per visualizzare i contenuti, solitamente il nero o il blu su uno sfondo chiaro. Sono ottimizzati per le esigenze di comunicazione di base e offrono un'ottima visibilità, una maggiore durata del prodotto e un consumo energetico efficiente. Questi display sono la soluzione ideale per i progetti in cui la funzionalità è più importante dell'estetica.
Multicolore
I display LCD multicolore visualizzano i contenuti in due o più colori predefiniti, migliorando l'organizzazione visiva e l'interazione con l'utente. Sono utili quando è necessario evidenziare indicatori di stato, avvisi o elementi di navigazione senza passare alla grafica a colori. Ciò li rende un ottimo compromesso tra la semplicità monocromatica e la funzionalità TFT a colori.
LCD a matrice passiva vs LCD a matrice attiva
Gli LCD a matrice passiva utilizzano una struttura semplice che aggiorna i pixel riga per riga. Ciò consente di mantenere bassi i costi e il consumo energetico, rendendoli una scelta intelligente per contenuti statici o a movimento lento. Gli LCD a matrice attiva, come quelli che utilizzano la tecnologia TFT, controllano ogni pixel individualmente. Ciò consente frequenze di aggiornamento più rapide, immagini più nitide e un'esperienza utente più fluida.
La decisione dipende dalla dinamicità dei contenuti visualizzati. Le immagini più complesse traggono vantaggio dalla matrice attiva, mentre le interfacce più semplici funzionano in modo affidabile con i modelli a matrice passiva.
Cose da considerare
Concentrati su come verrà utilizzato il display, cosa dovrà mostrare e dove verrà utilizzato. Adattare le caratteristiche all'uso reale aiuta a semplificare lo sviluppo e a migliorare le prestazioni del prodotto.
Personalizzazione
Gli LCD standard offrono una maggiore flessibilità di personalizzazione. Possono essere adattati per soddisfare esigenze specifiche in termini di dimensioni, interfaccia e montaggio senza richiedere una riprogettazione completa. Newhaven Display fornisce assistenza personalizzata per aiutare ad allineare le prestazioni del display agli obiettivi del vostro prodotto.
Utilizzo
I TFT sono ideali per prodotti che richiedono una risoluzione più elevata, una maggiore luminosità o funzionalità interattive. Gli LCD standard sono più adatti per applicazioni utilitaristiche in cui la priorità è data alla funzionalità, alla semplicità e all'efficienza.
Come pensi di gestire il display
Gli LCD standard funzionano bene con microcontrollori a basso costo. Non richiedono molta potenza, velocità o memoria. I TFT, invece, necessitano di hardware più potente per gestire velocità di trasmissione dati più elevate, resa dei colori e aggiornamento dello schermo.
Mito: i display TFT sono sempre più costosi dei display LCD standard
Fatto: Il costo dipende dal design, non solo dal tipo di display. Sebbene i TFT offrano funzionalità avanzate, un LCD standard con specifiche personalizzate o componenti aggiuntivi può eguagliare o superare tale costo. La scelta giusta dipende dalle esigenze e dalle priorità specifiche del prodotto.
Mito: l'LCD è una tecnologia obsoleta e in via di dismissione
Fatto: Gli schermi LCD continuano ad essere molto richiesti in tutti i settori industriali. Newhaven Display continua a produrre e fornire un'ampia gamma di opzioni LCD perché offrono prestazioni affidabili, lunga durata e convenienza economica. Per i progetti che privilegiano la stabilità, gli schermi LCD rimangono una scelta intelligente e affidabile.
Mito: tutti gli schermi LCD seguono gli standard industriali
Fatto: mentre gli schermi LCD standard tendono a seguire formati industriali uniformi, i display TFT spesso variano a seconda del produttore. Sono comuni differenze nelle interfacce, nei pinout e nei circuiti integrati dei driver. Comprendere queste variazioni in anticipo aiuta a garantire un processo di progettazione più fluido. Newhaven Display collabora con i team per identificare la soluzione più adatta ed evitare problemi di integrazione.
Conclusione
Gli schermi LCD rimangono una soluzione affidabile per un'ampia gamma di applicazioni. I pannelli monocromatici garantiscono efficienza e semplicità. I display TFT offrono immagini vivaci e una maggiore interattività. Comprendere il funzionamento di ciascun tipo, insieme alle differenze tra le tecnologie a matrice passiva e attiva, garantisce che il display sia in linea con i requisiti del vostro prodotto.
Per approfondire ulteriori fattori quali angoli di visione, requisiti di luminosità o modalità ottiche quali trasmissiva, transflettiva e riflettente, consulta la nostra guida ai tipi e alle modalità LCD.
Contatta Newhaven Display per scegliere il pannello LCD più adatto alla tua applicazione. Siamo qui per aiutarti con la nostra consulenza esperta e preventivi in giornata.


