Types of LCD
Sep 15th 2022
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screens are a staple in the digital display marketplace and are used in display applications across every industry. With every display application presenting a unique set of requirements, the selection of specialized LCDs has grown to meet these demands.
LCD screens can be grouped into three categories: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment). Each of these screen types has its own unique qualities, almost all of them having to do with how images appear across the various screen types.
In this article:
- TN (Twisted Nematic)
- VA (Vertical Alignment)
- IPS (In-Plane Switching)
- TN vs VA vs IPS Comparison Table
- Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
- Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
- Things to Consider
- Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
- Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
- Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
- Conclusion
Related: OLED vs LCD
It's worth noting that although these screen types belong to the LCD screen type, they use thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology which is a variant of the standard LCD screen type.
The main features that differentiate LCD screen types are brightness, viewing angles, color, and contrast.
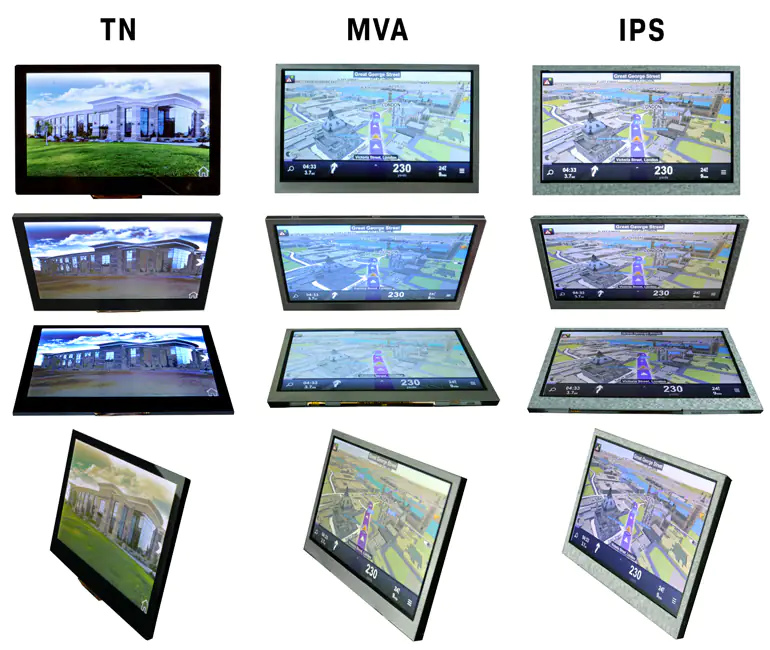
TN (Twisted Nematic)
This technology consists of nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. When power is applied to the electrodes, the liquid crystals twist 90°. TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs are the most common LCD screen type. They offer full-color images, and moderate viewing angles.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one, TN LCDs have faster response times and refresh rates than other TFT LCDs.
TN TFTs remain very popular among competitive PC gaming communities, where accuracy and response rates can make the difference between winning and losing.
Refresh rates and response times refer to the time it takes pixels to activate and deactivate in response to user inputs; this is crucial for fast-moving images or graphics that must update as fast as possible with extreme precision.
TN displays remain popular due to its reliable performance and cost-effective price point.
TN LCD Characteristics

-
Cost-Effective
Twisted nematic screens traditionally have been the most cost effect LCD option.
-
Highest Refresh Rates
TN LCD screens have the highest refresh rates and response times.
-
Limited Viewing Angles
TN LCD screens have average viewing angles of 45-65 degrees.
-
Limited Brightness
TN LCD screens are not bright enough for outdoor or direct sunlight viewing.
VA (Vertical Alignment)
VA, also known as Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment (MVA) dislays offer features found in both TN and IPS screens. The Pixels in VA displays align vertically to the glass substrate when voltage is applied, allowing light to pass through.
Displays with VA screens deliver wide viewing angles, high contrast, and good color reproduction. They maintain high response rates similar to TN TFTs but may not reach the same sunlight readable brightness levels as comparable TN or IPS LCDs. VA displays are generally best for applications that need to be viewed from multiple angles, like digital signage in a commercial setting.
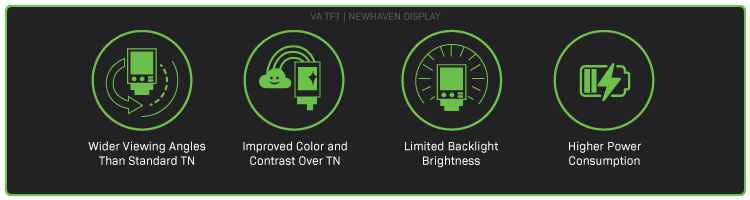
VA LCD Characteristics
-
Wide Viewing Angles
VA screens offer wider viewing angles than TN LCDs.
-
Colors & Contrast
VA LCD screens have improved color and contrast compared to TN TFTs.
-
Backlight Brightness
VA LCD screens tend to offer a lower brightness than an equivalent TN model TFT.
-
Power Consumption
Sunlight Readable LCDs can consume more energy than standard LCD screens.
IPS (In-Plane Switching)
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
Related: What is an IPS display?
IPS outperforms TN displays in every major category.
IPS is superior in contrast, brightness, viewing angles, and color representation compared to TN screens. Images on screen retain their quality without becoming washed out or distorted, no matter what angle they’re viewed from. Because of this, viewers have the flexibility to view content on the screen from almost anywhere rather than having to look at the display from a front-center position.
IPS makes it possible to get colorful, accurate, and sharp images viewed from almost any angle.
IPS displays offer a slightly lower refresh rate than TN displays. Remember that the time for pixels to go from inactive to active is measured in milliseconds. So for most users, the difference in refresh rates will go unnoticed.
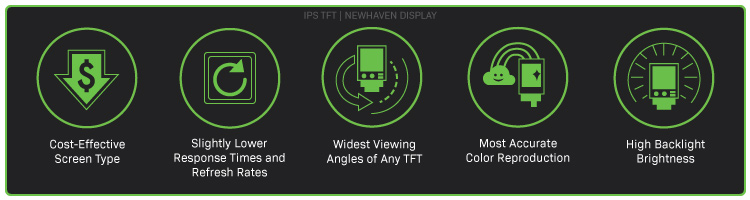
IPS LCD Characteristics
-
Price Point
IPS displays are now more cost effective comparable to TN LCDs.
-
Average Refresh Rates
IPS screens have slower refresh rates and response times than TN LCD screens.
-
Widest Viewing Angles
IPS LCD screens have the widest viewing angles of any TFT LCDs.
-
Best Colors
IPS LCD screens produce the most accurate, vivid colors of any TFT LCDs.
-
Highest Brightness
IPS LCD screens have high brightness backlights for sunlight readable environments.
TN vs VA vs IPS Comparison Table
| TN | VA | IPS | |
| Brightness | Better | Good | Best |
| Performance | Fastest | Fast | Fast |
| Viewing Angle | Good | Better | Best |
| Color | Good | Better | Best |
| Contrast | Good | Best | Better |
| Black Levels | Good | Best | Better |
| Picture Quality | Good | Better | Best |
| Uses | Gaming because of performance | General use because of price and quality | Professional where quality is required |
Standard LCDs vs. TFT LCDs
Standard LCDs are ideal for straightforward applications where simplicity, longevity, and low power consumption are key. TFT LCDs deliver enhanced visuals and interactivity, making them better suited for versatility or graphic-rich interfaces. Choosing between them depends on your project’s design priorities, environment, and user needs.
Monochrome
Monochrome LCDs use one color for display content, typically black or blue on a light background. They are optimized for basic communication needs, offering strong visibility, extended product life, and efficient power use. These displays are a reliable fit for designs where function matters more than form.
Multi-Color
Multi-color LCDs display content in two or more predefined colors, improving visual organization and user interaction. They are useful when you need to highlight status indicators, alerts, or navigation elements without moving to full-color graphics. This makes them a strong middle ground between monochrome simplicity and full-color TFT capability.
Passive vs Active Matrix LCDs
Passive matrix LCDs use a simple structure that updates pixels row by row. This keeps cost and power consumption low, making them a smart choice for static or slow-moving content. Active matrix LCDs, such as those using TFT technology, control each pixel individually. This allows for faster refresh rates, sharper images, and smoother user experiences.
The decision depends on how dynamic the display content is. More complex visuals benefit from active matrix, while simpler interfaces can perform reliably with passive matrix designs.
Things to Consider
Focus on how the display will be used, what it needs to show, and where it will operate. Matching features to real-world use helps streamline development and improve product performance.
Customization
Standard LCDs offer more flexibility for customization. They can be adapted to fit unique size, interface, and mounting needs without requiring a complete redesign. Newhaven Display provides custom support to help align display performance with your product goals.
Usage
TFTs are ideal for products that need higher resolution, brighter output, or interactive features. Standard LCDs are better suited for utilitarian applications where function, simplicity, and efficiency are the priority.
How You Plan to Drive the Display
Standard LCDs work well with lower-cost microcontrollers. They don’t require much power, speed, or memory. TFTs, on the other hand, need more capable hardware to handle higher data rates, color rendering, and screen refresh.
Myth: TFTs Are Always More Expensive Than Standard LCDs
Fact: Cost is driven by design, not just display type. While TFTs offer advanced features, a standard LCD with custom specs or added components can match or exceed that cost. The right choice depends on the product's specific needs and priorities.
Myth: LCD Is an Older, Phasing Out Technology
Fact: LCDs remain in high demand across industries. Newhaven Display continues to manufacture and supply a wide range of LCD options because they offer reliable performance, long product life, and cost efficiency. For designs that value stability, LCDs are still a smart and trusted choice.
Myth: All LCDs Follow Industry Standards
Fact: While standard LCDs tend to follow consistent industry formats, TFT displays often vary by manufacturer. Differences in interfaces, pinouts, and driver ICs are common. Understanding these variations early helps ensure a smoother design process. Newhaven Display works with teams to identify the right fit and avoid integration issues.
Conclusion
LCDs remain a reliable solution across a broad range of applications. Monochrome panels support efficiency and simplicity. TFT displays deliver vibrant visuals and greater interactivity. Understanding how each type functions, along with the differences between passive and active matrix technologies, ensures the display aligns with your product’s requirements.
To explore additional factors like viewing angles, brightness needs, or optical modes such as transmissive, transflective, and reflective, visit our LCD Types and Modes guide.
Get in touch with Newhaven Display to choose the right LCD panel for your application. We’re here to help with expert guidance and same-day quotes.


